Today, where information and data hold significant value, choosing the right storage solution is crucial. When it comes to portable storage devices, flash drives and solid-state drives (SSDs) are two popular options. Both offer the advantage of compactness and convenience, but they differ in terms of technology, performance, and use cases. In this blog post, we will delve into the characteristics of flash drives and SSDs, highlighting their pros and cons to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Flash Drive, and How Does it Work?
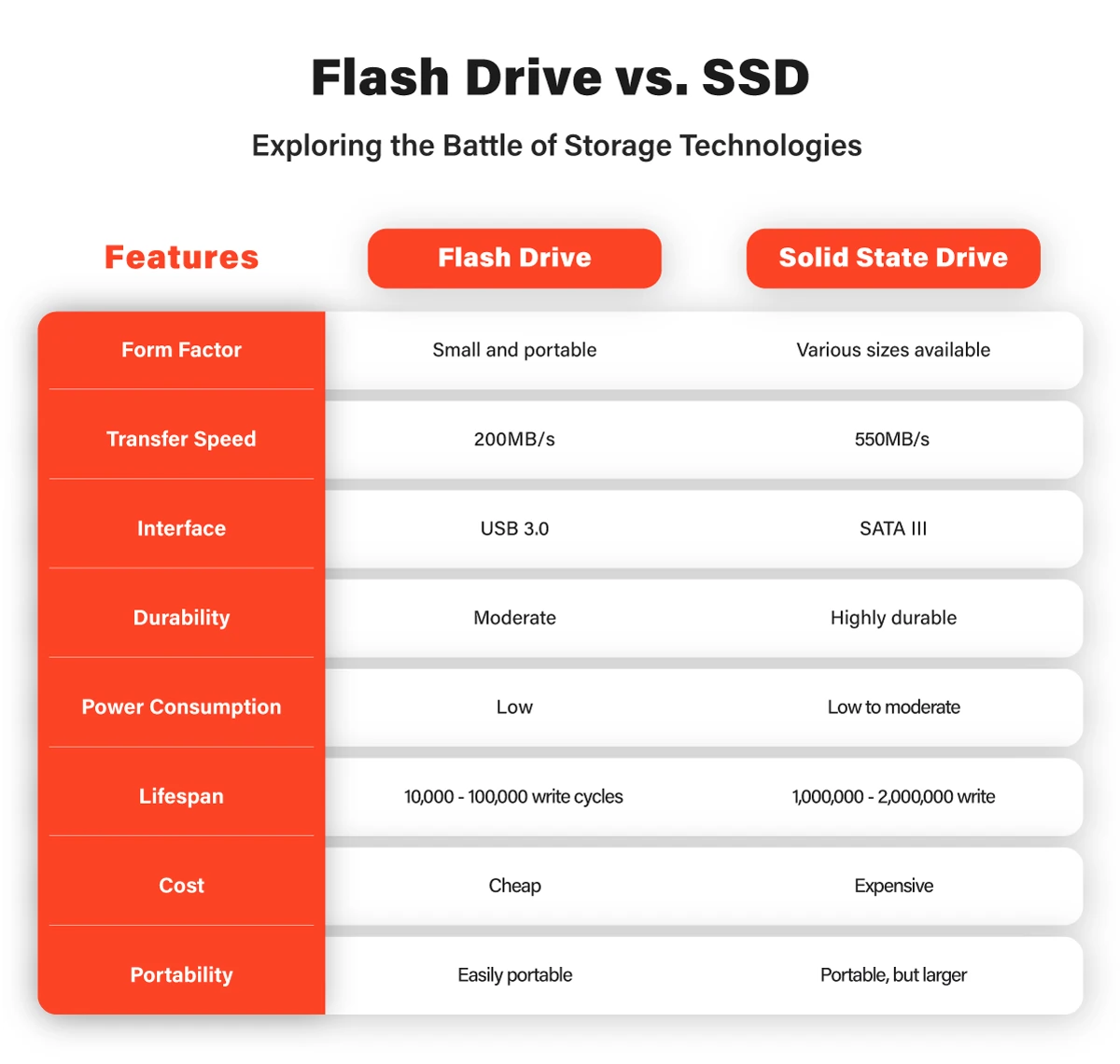
Flash drives, also known as USB drives, thumb drives, or memory sticks, are portable storage devices that connect to computers and other devices via a USB port. They consist of a printed circuit board (PCB) with embedded memory chips and a USB connector.

Flash drives use NAND flash memory technology, which allows for non-volatile storage of data. When you transfer or save files onto a flash drive, the data is stored in memory cells, and unlike traditional hard drives, there are no moving parts involved. This makes flash drives more resistant to physical damage and less prone to mechanical failures.
What is an SSD and How Does it Work?
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are storage devices that provide high-performance data storage using solid-state memory chips. Unlike flash drives, SSDs are available in various form factors, including the standard 2.5-inch drive for desktops and laptops, as well as smaller M.2 drives commonly used in ultrabooks and compact devices.

SSDs employ the same NAND flash memory technology found in flash drives but on a larger scale. They integrate a controller, which manages the data flow between the host device and the memory cells. This technology allows for faster data access and improved overall performance compared to traditional hard drives.
Flash Drive Pros and Cons
Flash drives, recognized for their portability, compatibility, durability, affordability, and user-friendly nature, have become integral for on-the-go data storage. However, their advantages are accompanied by certain limitations.
Pros:
Portability
Flash drives are small and lightweight, making them highly portable and convenient for carrying data on the go.
Compatibility
They are compatible with a wide range of devices, including computers, laptops, gaming consoles, and even some smart TVs.
Durability
Flash drives have no moving parts, making them more resistant to physical damage and shock.
Affordability
Flash drives are relatively inexpensive, making them an affordable storage option for everyday use.
Easy to use
Flash drives are plug-and-play devices, requiring no external power source or additional software installation.
Cons:
Limited storage capacity
Flash drives typically offer smaller storage capacities compared to SSDs, with higher-capacity options being more expensive.
Slower transfer speeds
While flash drives have improved over the years, they generally have slower read and write speeds compared to SSDs.
Lifespan
Flash drives have a limited number of read and write cycles, and frequent use can impact their lifespan.
In summary, while flash drives offer convenient and cost-effective storage solutions, users must consider trade-offs like limited storage capacity, slower transfer speeds, and a finite lifespan in making informed choices aligning with their specific needs.
SSD Pros and Cons
Solid State Drives (SSDs) stand out in storage solutions, offering enhanced performance with faster read and write speeds, expanded storage capacities, and superb reliability because of their lack of moving parts. However, like any technology, SSDs come with their considerations.
Pros:
Performance
SSDs provide significantly faster read and write speeds, resulting in improved system responsiveness and faster file transfers.
Larger storage capacity
SSDs are available in larger capacities, making them suitable for storing large files, multimedia content, and operating systems.
Reliability
With no moving parts, SSDs are more resistant to mechanical failures, offering a higher level of reliability and data protection.
Energy-efficient
SSDs consume less power than traditional hard drives, making them ideal for laptops and other battery-powered devices.
Compatibility
SSDs can be used as internal storage in desktops, laptops, and servers, as well as external storage via USB or Thunderbolt interfaces.
Cons:
Cost
SSDs tend to be more expensive than flash drives, especially for higher-capacity options.
Limited lifespan
Although SSDs have improved in terms of durability, they have a limited number of write cycles before performance degradation may occur.
Compatibility
While SSDs are compatible with most modern devices, some older systems may require additional adapters or connectors.
Flash Drive vs. SSD
When it comes to choosing between a flash drive and an SSD, it ultimately depends on your specific requirements and use cases. If you need a portable storage solution for everyday use, transferring files, or working on multiple devices, a flash drive is a cost-effective and convenient option.
On the other hand, if you prioritize performance, need larger storage capacities, or plan to use the storage device as the primary drive for your computer or server, an SSD would be a more suitable choice.
Flash drives and SSDs are both valuable storage technologies that have revolutionized the way we carry and store information. Flash drives excel in portability and affordability, while SSDs offer superior performance, reliability, and larger storage capacities.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each device will help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs. Whether you opt for a flash drive or an SSD, both solutions continue to play a vital role in modern computing, catering to a wide range of applications, from mobile devices to enterprise-grade data centers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a flash drive?
A flash drive, also known as a USB drive, thumb drive, or memory stick, is a portable storage device that uses flash memory technology to store and transfer data. It is typically a small, compact device that connects to computers and other devices via a USB port.
How does a flash drive work?
A flash drive consists of a printed circuit board (PCB) that houses memory chips and a USB connector. When you plug a flash drive into a USB port, the device establishes a connection with the computer or device. The data is then written to or read from the memory chips using the integrated controller on the flash drive. Flash drives are non-volatile, meaning they retain stored information even when disconnected from a power source.
Do SSDs have a limited lifespan?
Like any electronic device, SSDs have a limited lifespan. However, modern SSDs have improved durability and longevity. The lifespan of an SSD is determined by its endurance, which is measured by the number of write cycles the drive can handle before potential performance degradation occurs. Consumer-grade SSDs typically have sufficient endurance for everyday use, and their lifespan can be extended by adopting good storage practices and utilizing wear-leveling algorithms implemented by manufacturers.
Can I upgrade the storage capacity of a flash drive or an SSD?
Flash drives usually come with a fixed storage capacity that cannot be upgraded. However, with SSDs, some models offer upgrade options. In desktops and laptops, it is often possible to replace the existing SSD with a higher-capacity one. Additionally, some external SSDs come with replaceable storage modules, allowing you to upgrade the capacity as needed. However, it’s essential to check the compatibility and available upgrade options for your specific device before making any changes.
Which one is more durable, a flash drive or an SSD?
In terms of durability, both flash drives and SSDs have advantages over traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) due to their lack of moving parts. However, SSDs are generally considered more durable than flash drives. SSDs are built to withstand shock, vibrations, and temperature variations, making them more resistant to physical damage. Flash drives, although sturdy, can be more susceptible to physical wear and tear over time.
