In the ever-evolving world of technology, storage drives have seen remarkable advancements over the years. Two key players in the storage technology arena are PCIe SSDs and NVMe SSDs. These acronyms might sound like tech jargon, but they represent significant improvements in data transfer speeds and overall storage performance. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the realm of PCIe SSDs and NVMe SSDs, exploring their differences, benefits, and impact on modern computing.
Understanding PCIe SSDs and NVMe SSDs
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s break down the terms:
PCIe SSDs
PCIe stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express. This technology was originally developed as a means of connecting graphics cards to motherboards. However, its high bandwidth potential led to its adaptation for other purposes, including storage drives.
NVMe SSDs
NVMe, or Non-Volatile Memory Express, is a communication protocol designed explicitly for SSDs. Unlike traditional storage interfaces like SATA, NVMe is optimized for solid-state drives, reducing latency and maximizing throughput.
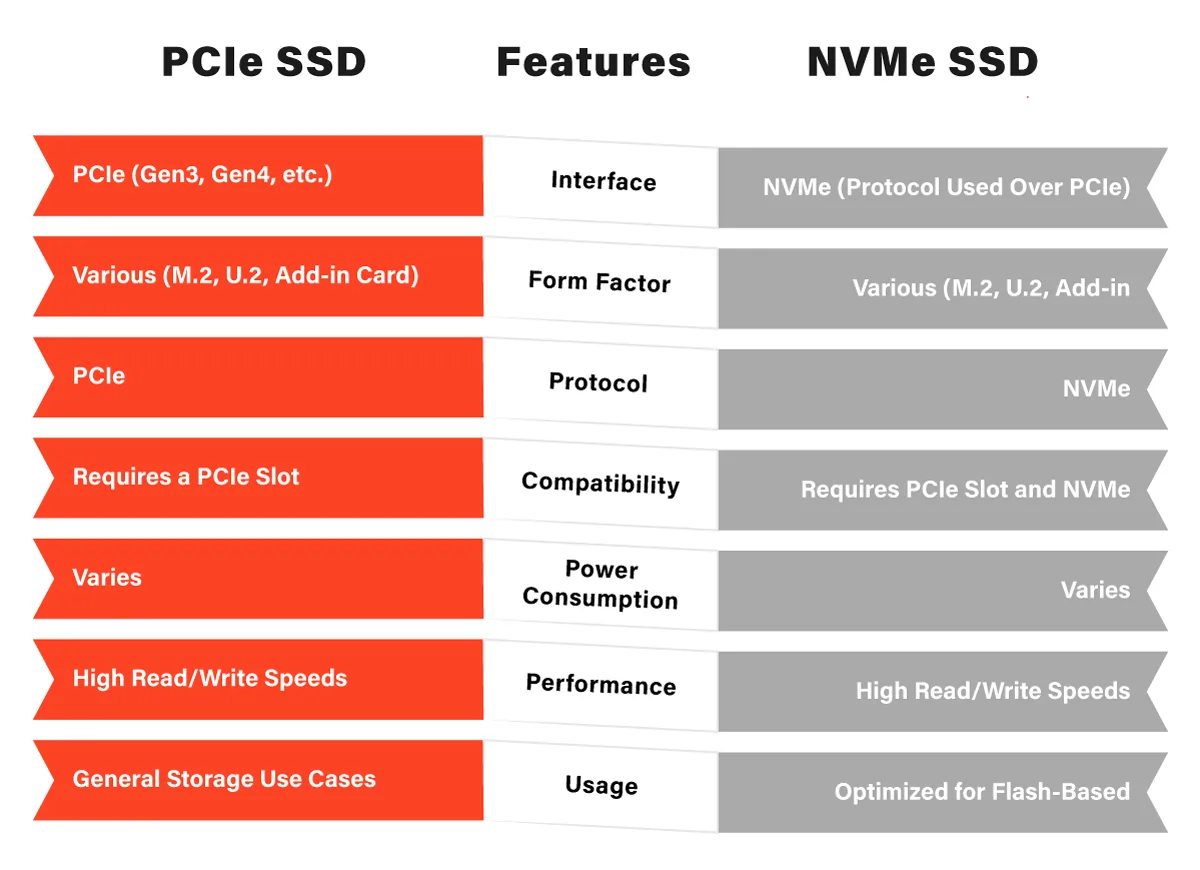
Form Factors and Connections
One of the critical differences between these storage technologies lies in their form factors and connections:
M.2 Slot
NVMe SSDs are typically found in M.2 slots on motherboards. M.2 is a compact, versatile form factor that connects directly to the motherboard, saving space in the process.
PCIe Connection
PCIe SSDs, on the other hand, connect directly to PCIe slots on the motherboard, which are commonly used for graphics cards and other expansion cards. This offers a higher level of flexibility and compatibility.
Communication Protocols and Speeds
The NVMe protocol is a game-changer when it comes to data transfer speeds and efficiency. The SATA interface limits traditional SATA SSDs, whereas NVMe SSDs leverage the PCIe connection for blazing-fast data transfer rates.

Transfer Speeds
NVMe-based SSDs can achieve mind-boggling transfer speeds, often exceeding 3,000 MB/s for sequential reads and writes. This far surpasses the capabilities of SATA SSDs, which generally top out at around 550 MB/s.
PCIe 3.0 and Beyond
PCIe 3.0, the third generation of the PCIe standard, is commonly used for these SSDs. However, PCIe 4.0 and even PCIe 5.0 have been introduced, further boosting transfer speeds and setting the stage for future advancements.
Benefits of NVMe and PCIe SSDs
Let’s explore the key benefits of NVMe and PCIe SSDs:
Reduced Latency
NVMe SSDs significantly reduce latency, leading to quicker response times and improved overall system performance.
Efficiency
The NVMe protocol optimizes the way data is processed, minimizing bottlenecks and ensuring more efficient utilization of storage resources.
High Throughput
PCIe SSDs leverage the PCIe bus, which provides higher bandwidth compared to the SATA interface, resulting in faster data transfers.
Future-Proofing
As technology evolves, the PCIe interface and NVMe protocol can be adapted to accommodate higher speeds, ensuring that your storage drive remains relevant for years to come.
In the realm of storage drives, NVMe SSDs and PCIe SSDs represent a seismic shift in performance and efficiency. While NVMe takes advantage of the lightning-fast PCIe connection, PCIe SSDs harness the raw power of the PCIe slot to deliver unparalleled data transfer speeds. These technologies have not only transformed the way we store and access data but also set the stage for more innovations in the future. So, whether you are a gamer, content creator, or professional, upgrading to an NVMe or PCIe SSD can unlock the true potential of your system’s storage capabilities and elevate your computing experience to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between PCIe SSD and NVMe SSD?
A PCIe SSD is a type of solid-state drive that connects using the PCIe slot on a computer’s motherboard. NVMe SSD, on the other hand, is a type of SSD that uses the NVMe protocol to communicate with the system. In simpler terms, PCIe is the connection, and NVMe is the protocol used for faster data transfer.
Are PCIe SSDs and NVMe SSDs the same thing?
Not exactly. PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a type of interface, like a highway, used to connect components to the motherboard. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a protocol or set of rules that SSDs use to communicate with the rest of the system. NVMe can be used over a PCIe connection to make SSDs faster and more efficient.
Which one is faster: PCIe SSD or NVMe SSD?
NVMe SSDs are typically faster because they use the NVMe protocol designed for quick data transfer. PCIe SSDs can use various protocols, including NVMe, but not all PCIe SSDs are NVMe-based. If an SSD is both PCIe and NVMe, it’s likely to be faster than one using only PCIe.
Should I choose a PCIe or NVMe SSD for my computer?
When it comes to choosing between PCIe and NVMe, it’s not an either/or situation. In most cases, you’ll find SSDs that are both PCIe and NVMe, offering the best of both worlds – the fast PCIe connection and the efficient NVMe protocol. So, if you’re looking for top-notch speed and performance, look for an SSD that supports both PCIe and NVMe.
