In the world of data storage, PCIe SSDs (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express Solid State Drives) have emerged as the ultimate solution, offering exceptional performance, speed, and reliability. With their lightning-fast transfer speeds and numerous advantages over traditional storage options, PCIe SSDs, particularly NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs, have become the go-to choice for tech enthusiasts and professionals alike. In this article, we will explore the benefits of PCIe SSDs, how they work, their advantages and potential disadvantages, and address concerns regarding data loss.
Understanding PCIe SSDs
PCIe SSDs, also known as NVMe SSDs, are solid-state drives that utilize the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) bus interface to connect directly to a computer’s motherboard. Unlike SATA SSDs, which connect via the SATA interface, PCIe SSDs offer faster data transfer rates and reduced latency due to the higher bandwidth of the PCIe interface.
PCIe SSD is a type of solid-state drive that leverages the PCIe bus interface, enabling faster data transfer speeds and improved performance compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
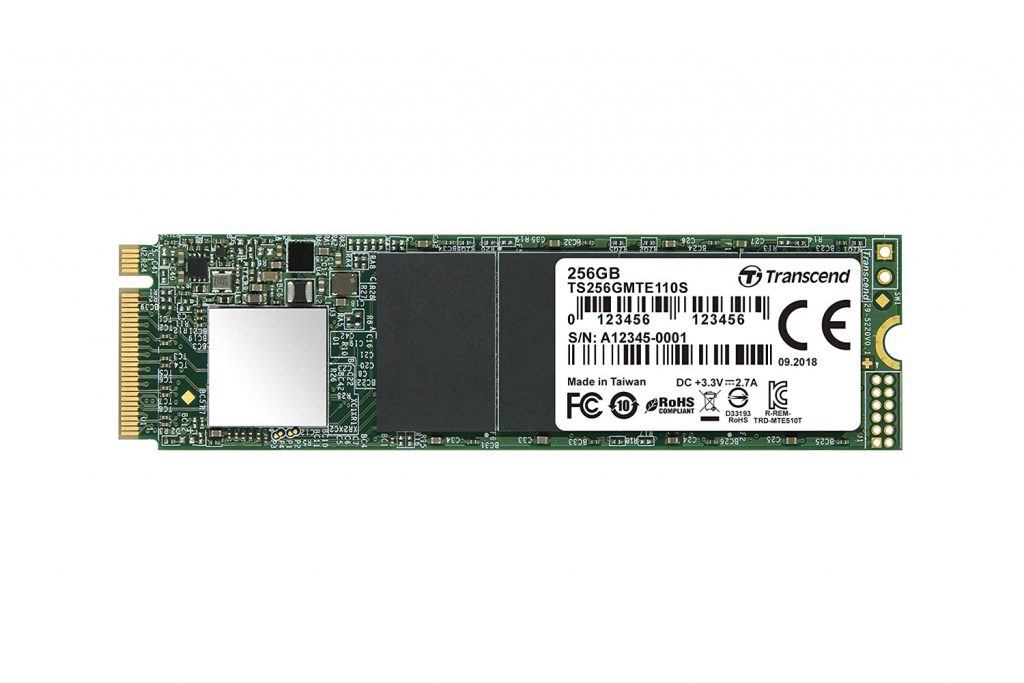

It uses flash memory technology to store and retrieve data, similar to other types of SSDs.PCIe SSDs work by connecting directly to the PCIe slot on a computer’s motherboard.
This direct connection provides a dedicated pathway for data transfer between the SSD and the processor, bypassing the limitations of the SATA interface. The NVMe protocol further enhances performance by optimizing data transfer processes and reducing latency.
Advantages of PCIe SSDs
Blazing-Fast Transfer Speeds
PCIe SSDs offer exceptional transfer speeds, surpassing the capabilities of SATA SSDs. Leveraging the high-bandwidth PCIe interface, PCIe SSDs can achieve sequential read and write speeds of several gigabytes per second, significantly reducing data access times and improving overall system performance.
Enhanced Performance with NVMe Technology
NVMe, a communication protocol designed specifically for flash-based storage devices, optimizes data transfer processes. It maximizes the potential of flash memory technology by reducing latency and enabling efficient parallelism and multiple queues. This results in improved system responsiveness and faster data access.

Versatility and Form Factors
PCIe SSDs come in various form factors, making them compatible with different systems and devices. They are available in M.2 and add-in card form factors, allowing for easy integration into desktops, laptops, and workstations.
Improved Battery Life
PCIe SSDs are engineered to be power-efficient, consuming less power compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and even SATA SSDs. This is especially beneficial for laptops and portable devices, where battery life is crucial.
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Blazing Fast Speeds | PCIe SSDs offer significantly faster data transfer rates compared to traditional SATA SSDs or HDDs. |
| Low Latency | Reduced latency ensures quick data access and minimal delays, making them ideal for real-time tasks. |
| Enhanced Performance | High-speed PCIe interfaces improve overall system performance, particularly during data-intensive tasks. |
| Energy Efficiency | PCIe SSDs are often more power-efficient, leading to longer battery life for laptops and lower energy costs for desktops. |
| Compact Form Factors | Their small form factors, like M.2 and U.2, save space in laptops and allow for more storage options in desktops. |
| Scalability | Many PCIe SSDs support NVMe, enabling the use of multiple SSDs in RAID configurations for increased storage and performance. |
| Ideal for Gaming | PCIe SSDs reduce game load times, providing a smoother gaming experience with shorter loading screens. |
| Compatibility | PCIe SSDs are compatible with a wide range of devices, from laptops and desktops to workstations and servers. |
Disadvantages of PCIe SSDs
Higher Costs
PCIe SSDs are usually higher than SATA SSDs, as they offer more advanced technology and better performance. Nevertheless, the prices have been gradually decreasing, which is making them more affordable and available to a larger number of users.
Compatibility
Older systems may not support PCIe SSDs or may require specific PCIe versions, such as PCIe 3.0 or higher, to achieve optimal performance. It is essential to check the compatibility of your system’s motherboard before purchasing a PCIe SSD.
| Disadvantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Cost | PCIe SSDs are generally more expensive per gigabyte compared to traditional HDDs or SATA SSDs. |
| Limited Compatibility | Some older systems may lack PCIe slots, limiting the upgrade options for users with legacy hardware. |
| Limited Storage Capacities | High-capacity PCIe SSDs can be costly, and capacities may not match those of larger HDDs. |
| Heat Generation | PCIe SSDs can generate more heat than other storage options, necessitating efficient cooling solutions. |
| Potential for Data Loss on Power Failure | Some consumer-grade PCIe SSDs may lack power-loss protection, increasing the risk of data loss in case of sudden power outages. |
Data Loss on PCIe SSDs: Common Causes
As with any storage device, PCIe SSDs are not immune to the risk of data loss. While they offer exceptional performance and reliability, it is important to be aware of potential factors that can lead to data loss and take proactive measures to mitigate these risks. In this section, we will explore the common causes of data loss on PCIe SSDs and discuss strategies to protect your valuable data.
Hardware Failures
Hardware failures can occur in any storage device, including PCIe SSDs. Components such as NAND flash memory chips, controller chips, or other electronic components can experience malfunctions or failures over time. These failures can result in data corruption or complete data loss. To minimize the risk, it is recommended to choose high-quality PCIe SSDs from reputable manufacturers that offer reliable and durable components.
Accidental Deletions and Formatting
Human error can lead to accidental deletion or formatting of data on a PCIe SSD. Whether it is mistakenly deleting an important file or formatting the drive without a backup, these actions can result in permanent data loss.
To prevent accidental data loss, it is crucial to practice safe data management habits. Create regular backups of your important files on separate storage devices or cloud services
Power Outages and Surges
Power interruptions or sudden voltage surges can cause data loss or corruption on PCIe SSDs. When power is abruptly cut off during a write operation, data being written may become incomplete or corrupted. Similarly, voltage surges can damage the electronic components of the SSD. To safeguard against such events, using an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or surge protector can provide a reliable power source and protect your PCIe SSD from sudden power-related issues.
Firmware or Software Issues
PCIe SSDs rely on the firmware to control their operations and ensure optimal performance. However, firmware bugs or compatibility issues with the system’s operating system or other software can lead to data loss or corruption. Keeping your PCIe SSD’s firmware up to date is essential to benefit from bug fixes, performance enhancements, and improved compatibility with various systems.
Environmental Factors
Extreme temperatures, moisture, or physical damage can also contribute to data loss on PCIe SSDs. Exposing the SSD to excessive heat or cold, liquids, or physical impacts can lead to the failure of internal components and data loss. To protect your PCIe SSD, ensure it is installed in a well-ventilated area and away from direct exposure to liquids. Handle the drive with care to avoid physical damage.
Mitigating the Risk of Data Loss on PCIe SSDs
Regular Data Backups
Creating regular backups of your important data is crucial. Store backups on separate storage devices or utilize cloud backup services to ensure data redundancy and easy restoration in case of data loss.
Data Recovery Services
In the unfortunate event of data loss, specialized professional data recovery services may help retrieve lost data. These solutions are designed to recover data from various storage devices, including PCIe SSDs.
Firmware Updates
Keep your PCIe SSD’s firmware up to date by regularly checking for firmware updates from the manufacturer’s website. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can enhance the reliability and stability of the SSD.
Safe Data Management Practices
Practice safe data management habits, such as verifying before performing critical operations, maintaining multiple copies of important files, and avoiding unnecessary data deletions or formatting.
PCIe SSDs, particularly NVMe SSDs, offer unmatched performance, speed, and reliability, making them the ultimate storage solution for demanding users. With their blazing-fast transfer speeds, enhanced performance with NVMe technology, versatility in form factors, and improved battery life, PCIe SSDs deliver exceptional storage performance for a wide range of applications. While they may come at a slightly higher cost and require compatibility considerations, the benefits of PCIe SSDs outweigh the potential drawbacks, positioning them as the preferred choice for users seeking top-tier storage solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a PCIe SSD?
A PCIe SSD, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express Solid State Drive, is a storage device that utilizes the PCIe bus interface to connect directly to a computer’s motherboard. It offers faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to traditional SATA SSDs, resulting in improved overall system performance.
How do I install a PCIe SSD in my computer?
Installing a PCIe SSD involves inserting the SSD into an available PCIe slot on your motherboard. Most modern motherboards have M.2 slots specifically designed for PCIe SSDs. If you’re using an add-in card (AIC) form factor PCIe SSD, you’ll need to insert the card into an appropriate PCIe slot. It’s important to consult your motherboard’s manual and ensure compatibility with the specific PCIe version and form factor of the SSD.
How does a PCIe SSD differ from a SATA SSD?
The main difference between a PCIe SSD and a SATA SSD lies in the interface used for connection. While SATA SSDs connect via the SATA interface, PCIe SSDs directly connect to the PCIe slot on the motherboard. This direct connection allows for higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates, making PCIe SSDs significantly faster than SATA SSDs.
Are all PCIe SSDs the same?
No, PCIe SSDs come in different form factors and performance levels. The form factor of a PCIe SSD determines its physical dimensions and compatibility with different devices. Common form factors include M.2 and add-in card (AIC). Additionally, PCIe SSDs vary in terms of their performance, such as transfer speeds, storage capacities, and endurance ratings. It’s essential to choose a PCIe SSD that matches your specific requirements and is compatible with your system.
Can I use multiple PCIe SSDs in a RAID configuration?
Yes, it is possible to set up multiple PCIe SSDs in a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configuration to improve performance or data redundancy. However, the ability to create a RAID array depends on your motherboard’s RAID capabilities and the specific RAID levels supported. Consult your motherboard’s documentation and RAID controller specifications for more information on setting up a RAID configuration with PCIe SSDs.
