In the ever-evolving landscape of storage devices, solid-state drives (SSDs) have emerged as the go-to choice for faster and more reliable data storage. Among the various types of SSDs available, the M.2 SSD has gained significant popularity for its compact form factor, high performance, and versatility. If you’re new to the world of M.2 SSDs and want to learn more, you’ve come to the right place. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore what an M.2 SSD is, how it works, its advantages, disadvantages, data loss risks, and data recovery solutions.
What is an M.2 SSD?
An M.2 SSD is a type of solid-state drive that utilizes the M.2 form factor for its design. The M.2 form factor is a small, rectangular, and slim design that is commonly used in modern computers and laptops. The M.2 SSD gets its name from the M.2 slot, where it is inserted on the motherboard. Compared to traditional 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs take up less space, allowing for sleeker and more compact device designs. They are ideal for thin laptops, ultrabooks, and small form factor desktops.
M.2 SSDs rely on flash memory technology for data storage. Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory that retains data even when the power is turned off. This makes M.2 SSDs more durable and reliable compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), which have moving mechanical parts that are prone to failure. Flash memory also enables faster data access, resulting in improved performance.
M.2 SSDs can utilize different interfaces, such as Serial ATA (SATA) or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe), to connect to the computer’s motherboard. SATA-based M.2 SSDs offer sequential read and write speeds of up to 550MB/s and 500MB/s, respectively, while PCIe-based M.2 SSDs can achieve much higher speeds, with some models reaching sequential read and write speeds of over 3000MB/s.
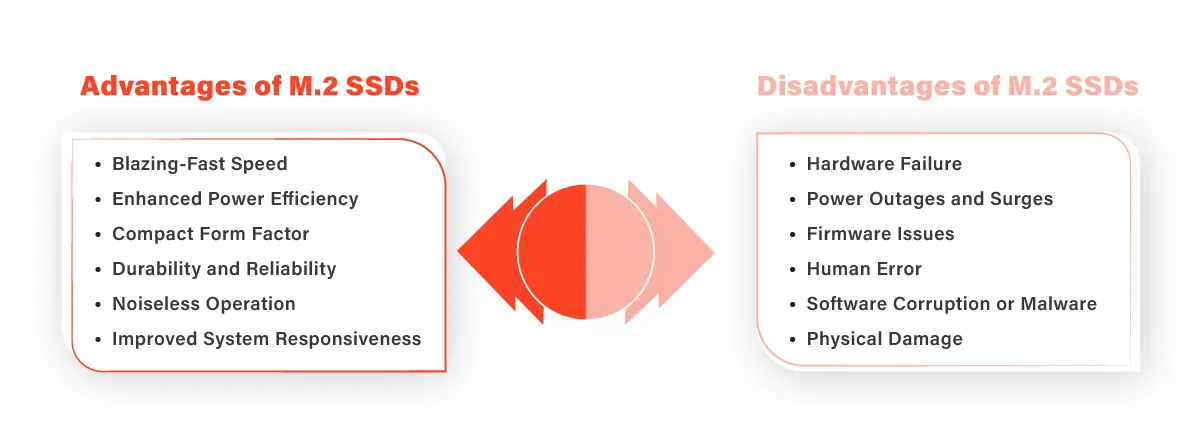
Advantages of M.2 SSDs
M.2 SSDs offer several advantages over traditional storage options. Here are six key benefits of using an M.2 SSD:
Blazing-Fast Speed
M.2 SSDs provide significantly faster data transfer speeds than traditional hard drives (HDDs) and even SATA-based SSDs. By leveraging the PCIe interface, M.2 SSDs can achieve incredibly high sequential read and write speeds, resulting in lightning-fast boot times, application launches, and file transfers. This translates to a snappier computing experience and reduced waiting times.

Enhanced Power Efficiency
M.2 SSD consume less power compared to traditional hard drives, leading to improved energy efficiency. This is particularly beneficial for laptops, as it helps prolong battery life and allows for longer usage on a single charge. Additionally, reduced power consumption contributes to lower heat generation, which can positively impact the overall system’s temperature and performance.
Compact Form Factor
M.2 SSDs are designed to be compact and slim, making them an ideal storage solution for modern devices with limited space, such as thin laptops, ultrabooks, and small form factor desktops. Their small size allows for sleeker device designs, improved airflow, and better utilization of available space inside the system.
Durability and Reliability
M.2 SSDs rely on flash memory technology, which has no moving parts. Unlike traditional hard drives with spinning platters, M.2 SSDs are less susceptible to physical damage caused by shock, vibration, or accidental drops. The absence of mechanical components also means reduced wear and tear, resulting in improved reliability and longevity.
Noiseless Operation
With no moving parts, M.2 SSDs operate silently, providing a noiseless computing environment. This is especially advantageous for users who prioritize a quiet workspace or require noise-sensitive applications, such as audio recording or video editing.
Improved System Responsiveness
By upgrading to an M2 SSD, you can significantly improve the overall responsiveness of your system. The faster data access and transfer speeds offered by M.2 SSDs enable applications to load quicker, files to open faster, and tasks to be completed more efficiently. Whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or business professional, an M.2 SSD can greatly enhance your productivity and user experience.
Disadvantages of M.2 SSDs
While M.2 SSDs offer numerous advantages, it is important to consider their limitations as well. Here are six disadvantages of using an M.2 SSD:
Higher Cost
M.2 SSDs tend to be more expensive than traditional hard drives (HDDs) and even SATA-based SSDs. The advanced technology, compact form factor, and faster speeds of M.2 SSDs contribute to their higher price point. This can be a deterrent for budget-conscious users who prioritize cost-effectiveness over performance.
Compatibility Concerns
M.2 slots may not be available on older motherboards or certain low-end devices. Before investing in an M.2 SSD, it is crucial to check your system’s compatibility and ensure that your motherboard supports the M.2 form factor. In some cases, an additional adapter or PCIe card may be required to use an M.2 SSD, adding complexity and potential cost to the upgrade process.

Heat Dissipation
M.2 SSDs have a tendency to generate more heat compared to traditional storage devices. The compact design of M.2 SSDs limits the space for heat dissipation, which can potentially lead to higher operating temperatures. If not properly cooled, excessive heat can cause thermal throttling, resulting in performance degradation and reduced lifespan of the SSD.
Limited Storage Capacity
M.2 SSDs generally offer smaller storage capacities compared to traditional hard drives. While higher-capacity M.2 SSDs are available, they can be quite expensive. If you require a large amount of storage space, such as for media files or extensive software libraries, you may find that the cost per gigabyte of an M.2 SSD is prohibitive.
Risk of Data Loss
Like any storage device, M.2 SSDs are not immune to data loss risks. Power outages, physical damage, firmware issues, or accidental deletion can lead to data loss on an M.2 SSD. It’s crucial to maintain regular backups of your important data to mitigate the impact of potential data loss.
Limited Upgrade Potential
If your system lacks an available M.2 slot, upgrading to an M.2 SSD may not be feasible without significant modifications or a complete system overhaul. This limitation can restrict the upgrade options for certain systems, especially older computers or budget-oriented devices.
Data Loss Risks on M.2 SSDs
Data loss is a potential risk that users should be aware of when utilizing any storage device, including M.2 SSDs. While M.2 SSDs offer numerous advantages, it is important to understand the factors that can contribute to data loss and take appropriate measures to mitigate these risks. Here are some common data loss risks associated with M.2 SSDs:

Hardware Failure
Although M.2 SSDs are generally more reliable than traditional hard drives (HDDs) due to their lack of moving mechanical parts, they are not immune to hardware failures. Over time, electronic components or memory cells within the SSD can fail, resulting in data loss. Common hardware failures include controller failures, NAND flash chip malfunctions, or issues with the PCB (Printed Circuit Board).
Power Outages and Surges
Abrupt power outages or power surges can pose a risk to the data stored on an M.2 SSD. Sudden power loss during read or write operations can lead to data corruption or incomplete writes, potentially rendering the affected files or even the entire SSD inaccessible.
Firmware Issues
Firmware, which acts as an SSD’s operating system, can occasionally encounter issues or bugs that may cause data loss or device malfunction. Manufacturers release firmware updates to address such issues, and it is crucial to regularly update the SSD firmware to ensure optimal performance and security.
Human Error
Human error can cause accidental deletion, formatting, or overwriting of important files. Without a proper backup strategy, these actions can result in permanent data loss on the M.2 SSD.
Software Corruption or Malware
Malware infections, software bugs, or system crashes can corrupt data on an M.2 SSD. This can occur if critical system files or user data are compromised or overwritten by malicious software or faulty applications.
Physical Damage
While M. 2 SSDs are more durable than HDDs, they can still be susceptible to physical damage if mishandled or subjected to extreme conditions. Dropping the device, exposing it to excessive heat or moisture, or other physical trauma can make the SSD inaccessible and the data irretrievable.
Mitigating the Risk of Data Loss
To mitigate the risk of data loss on M.2 SSDs, consider the following precautions:
- Regular Backups: Implement a robust backup strategy by creating regular backups of important files stored on the M.2 SSD. This can be done by utilizing external storage devices, cloud backup solutions, or dedicated backup software.
- Surge Protection: Use a reliable surge protector or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to safeguard the M.2 SSD and the entire system against sudden power outages or power surges.
- Firmware Updates: Stay updated with the latest firmware releases provided by the SSD manufacturer. Regularly check for firmware updates and apply them to ensure the SSD’s stability, performance, and security.
- Data Recovery Services: In the unfortunate event of data loss on an M.2 SSD, professional data recovery services may be able to help. Data recovery experts possess the necessary expertise and specialized tools to recover lost or inaccessible data from damaged or failed M.2 SSDs.
- Proper Handling: Handle the M.2 SSD with care, avoiding drops, excessive bending, or exposing it to extreme temperatures, moisture, or static electricity. Follow best practices for hardware installation and maintenance to minimize the risk of physical damage.
By taking these precautions and being mindful of the potential risks, users can minimize the likelihood of data loss on M.2 SSDs and ensure the safety and security of their valuable data.
M.2 SSDs have revolutionized the storage industry with their compact design, blazing-fast performance, and numerous advantages. They offer significant improvements in speed, space efficiency, power efficiency, and durability over traditional storage options. However, they come with some disadvantages, including cost and compatibility concerns. Additionally, data loss risks are inherent to any storage device, and M.2 SSDs are no exception. It is crucial to maintain regular backups and seek professional data recovery assistance in case of data loss. With careful consideration and appropriate measures, M.2 SSDs can provide a reliable and efficient storage solution for your computing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an M.2 SSD and a traditional 2.5-inch SATA SSD?
M.2 SSDs and traditional 2.5-inch SATA SSDs differ in their form factor and interface. M.2 SSDs are smaller, slim, and connect directly to the motherboard via an M.2 slot, while 2.5-inch SATA SSDs are larger and connect via SATA cables. M.2 SSDs often offer faster speeds and more compact designs, making them suitable for thin laptops and small form factor systems.
Are M.2 SSDs compatible with all motherboards?
M.2 SSD compatibility depends on the motherboard’s specifications. Some motherboards support both SATA and PCIe-based M.2 SSDs, while others may only support one type. It’s important to check the motherboard’s documentation to determine the supported types and keying of M.2 slots. Additionally, the length of the M.2 SSD module should match the available space on the motherboard.
Can I use an M.2 SSD as the primary boot drive?
Yes, M.2 SSDs can be used as the primary boot drive. They offer faster boot times compared to traditional hard drives and can significantly improve overall system performance. By installing the operating system and essential applications on the M.2 SSD, you can experience quicker startup and application loading times.
Can I transfer data from my existing storage drive to an M.2 SSD?
Yes, you can transfer data from your existing storage drive to an M.2 SSD. There are several methods to do this, including using data migration software or manually copying files. Data migration software simplifies the process by cloning the entire drive, including the operating system, applications, and data, to the new M.2 SSD. However, it’s essential to ensure that the capacity of the M.2 SSD is sufficient to accommodate all the data from the existing drive.
Are M.2 SSDs only for high-end systems and gaming?
While M.2 SSDs are often associated with high-end systems and gaming due to their faster speeds, they are suitable for a wide range of computing needs. M.2 SSDs can benefit any user seeking improved storage performance, including professionals working with large datasets, content creators working with high-resolution media, or everyday users looking for faster system responsiveness. M.2 SSDs come in a variety of capacities, making them accessible for different budget ranges and storage requirements.
