Solid State Drives (SSDs) have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their speed and reliability. However, there are still concerns about their failure rates compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). In this blog post, our team will compare SSD and HDD failure rates and discuss some factors contributing to these rates.
SSD Failure Rates
One of the main benefits of SSDs is that they have no moving parts, which means they are less prone to mechanical failures than HDDs. However, SSDs still have a limited lifespan and can fail due to various factors, such as electrical issues, firmware issues, or wear and tear.
A study conducted by Backblaze, a cloud storage provider, found that the overall annual failure rate for SSDs was 1.6%, compared to 7.7% for HDDs. The study also found that the failure rate for SSDs increased as they got older, with drives over three years old having a failure rate of 2.2%. However, even with this increase, the failure rate for older SSDs was still significantly lower than that of HDDs.
Another study conducted by Tom’s Hardware found similar results. The study found that the overall failure rate for SSDs was 0.5%, compared to 2.5% for HDDs. The study also found that the failure rate for SSDs increased as they got older, with drives over four years old having a failure rate of 1.2%.
Overall, these studies suggest that SSDs have a lower failure rate than HDDs. However, it is important to note that these studies were conducted on a specific set of SSD models and may not represent all SSDs and HDDs.
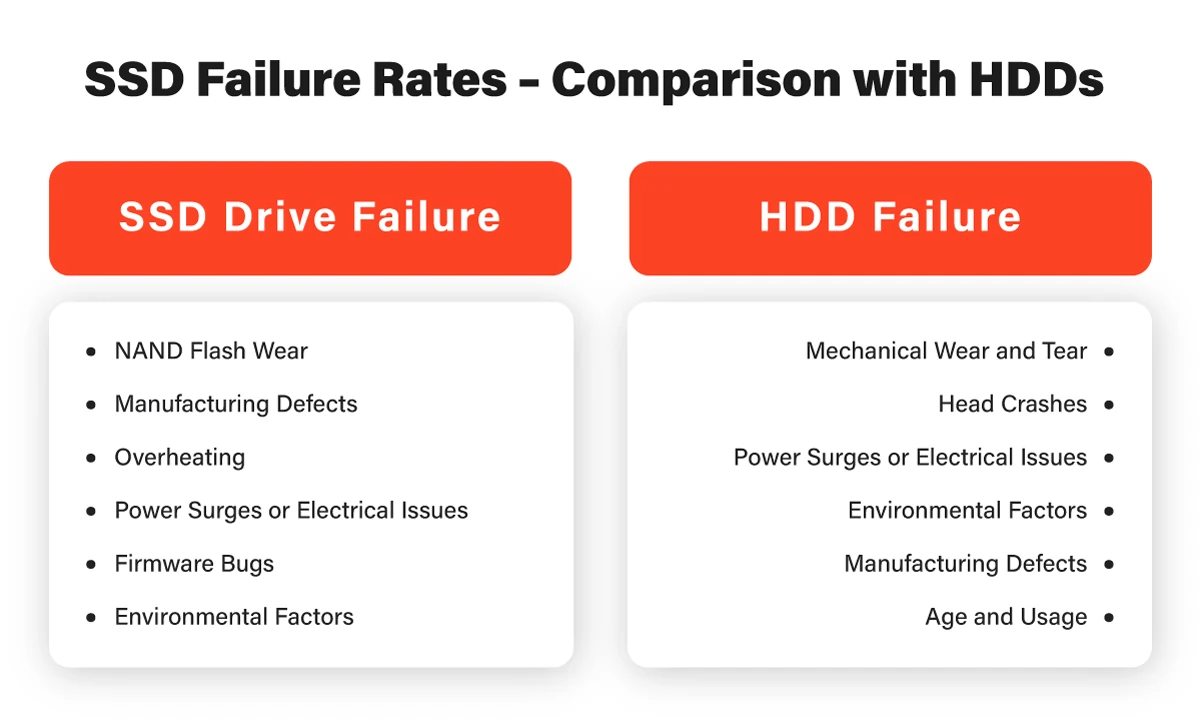
Factors Contributing to SSD Drive Failure Rates
NAND Wear. SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data. Over time, this memory can wear out, leading to data corruption and failure. However, most modern SSDs use wear-leveling algorithms to distribute writes evenly across the drive, which can help reduce wear’s impact.
Firmware Issues. Like all computer components, SSDs rely on the firmware to function properly. If there are issues with the firmware, it can lead to malfunction. However, firmware issues are relatively rare and usually addressed through updates.

Electrical Issues. SSDs can also fail due to electrical issues such as power surges or voltage fluctuations. However, most SSDs have built-in protection mechanisms to help prevent these types of failures.
Manufacturing Defects. Like all computer components, SSDs can be prone to manufacturing defects. However, these types of failures are relatively rare and are usually covered under warranty.
HDD Failure Rates
HDDs have been around for decades and are a tried and tested technology. However, they have several moving parts, including spinning platters and read/write heads, making them more prone to mechanical failures than SSDs.
A study conducted by Backblaze found that the overall annual failure rate for HDDs was 7.7%. The study also found that the failure rate for HDDs increased as they got older, with drives over three years old having a failure rate of 12.5%.
Another study conducted by Tom’s Hardware found similar results. The study found that the overall failure rate for HDDs was 2.5%, with drives over four years old having a failure rate of 5%.
These studies suggest that HDDs have a higher failure rate than SSDs, particularly as they age. This is largely due to the mechanical components of HDDs, which are more prone to wear and tear. These were the results of comparing SSD failure rate vs HDD, but when choosing a device for your appliance, not only SSD vs hard drive failure rates should be considered.
Factors Contributing to HDD Failure
Mechanical Issues. As mentioned earlier, HDDs have spinning platters and read/write heads, which makes them more prone to mechanical failures. Common mechanical failures include motor failure, head crashes, and platter damage.
Environmental Factors. HDDs can also fail due to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and vibration. These factors can cause damage to the mechanical components of the drive or affect the read/write heads.

Power Surges. Power surges can cause damage to the electronics in an HDD, leading to drive failure. However, most modern HDDs have built-in protection mechanisms to help prevent these types of losses.
Manufacturing Defects. Like all computer components, HDDs can be prone to manufacturing defects. These types of failures are relatively rare and are usually covered under warranty. Nevertheless, when comparing SSD vs. HDD failure rates, this factors is the same.
Failure Rate of SSD vs. HDD
When choosing between HDD vs SSD in failure rate, there are several factors to consider. SSDs are more reliable than HDDs and are generally faster but they are also more expensive. HDDs are slower and less reliable than SSDs but are also more affordable.
If you are looking for a drive that can store a large amount of data at a low cost, then an HDD may be the better choice. However, if you are looking for a drive that can provide fast performance and reliability, then an SSD may be a more suitable option.
Ultimately, the choice between SSDs and HDDs comes down to personal preference and the specific needs of the user. Regardless of which type of drive you choose, it is important to back up your data regularly to prevent loss in the event of a drive failure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which type of drive is more reliable, SSD or HDD?
Generally, SSDs have a lower failure rate than HDDs due to their lack of moving parts. However, the failure rate can vary depending on the brand, model, and usage of the drive.
How long do SSDs and HDDs last before they fail?
The lifespan of a drive can vary depending on several factors, including usage, temperature, and quality of manufacturing. On average, HDDs can last up to 5-7 years, while SSDs can last up to 10 years or more.
What are the most common causes of failure for SSDs and HDDs?
For HDDs, the most common causes of failure are mechanical issues such as head crashes and motor failures. For SSDs, the most common causes of failure are firmware issues, electronic component failures, and bad sectors.
What can I do to prolong the lifespan of my drive?
To prolong the lifespan of your drive, you can take several precautions such as keeping your drive free of dust and debris, avoiding exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity, and using a reputable brand and model of drive. It is also important to regularly back up your data to avoid permanent loss in case of drive failure.
Should I choose an SSD or HDD for my storage needs?
The choice between SSD and HDD depends on your specific needs and budget. SSDs offer faster read and write speeds and a lower risk of failure, but they are more expensive per GB of storage. HDDs offer more storage for less money, but they are slower and have a higher risk of failure. It is recommended to research and compare different brands and models before making a decision.