Data protection is a critical consideration for any organization or individual storing valuable information. Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID) provide a means of enhancing data protection through various RAID levels. Two commonly used RAID levels, RAID 6 and RAID 10, offer distinct advantages and disadvantages when it comes to disk capacity, disk utilization, data loss prevention, and rebuild capabilities. In this article, we will delve into the details of RAID 6 and RAID 10, comparing their functionalities and assessing which option may be more suitable for your data protection needs.
Understanding RAID Levels
RAID levels play a crucial role in determining the performance and data protection capabilities of a storage system. RAID 6 and RAID 10 are two popular options that provide different configurations for data storage and redundancy. Let’s explore each of these RAID levels in more detail.
Understanding RAID 6
RAID 6, also known as block-level striping with double parity, offers enhanced data protection compared to other RAID configurations. It requires a minimum of four disks and can sustain up to two simultaneous disk failures without any data loss.
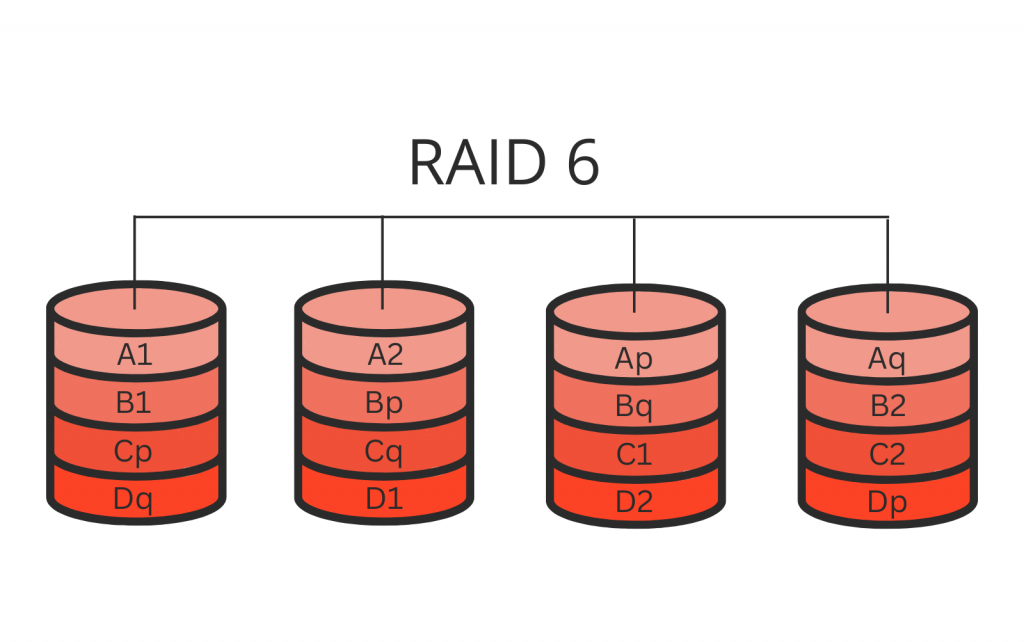
RAID 6 calculates parity information for data blocks and writes it to two disks within the array. RAID 6 employs a distributed parity scheme where data and parity blocks are spread across all the drives in the array. This enables the system to rebuild the array even if multiple disks fail. The parity calculations in RAID 6 are more complex than in other RAID levels, which slightly affects the write performance. However, it still provides good read performance.
Advantages of RAID 6
Fault Tolerance
RAID 6 can withstand the failure of two disks simultaneously, ensuring data integrity and availability.
Large Disk Capacity
RAID 6 allows for high disk capacity utilization, as it can efficiently handle arrays with many drives.
Data Protection
With dual parity, RAID 6 significantly reduces the risk of data loss during disk failures.
Redundancy
The double parity in RAID 6 provides an additional layer of redundancy compared to other RAID levels.
Disadvantages of RAID 6
Write Performance
Due to the complex parity calculations, RAID 6 tends to have lower write performance compared to other RAID configurations.
Rebuild Times
Rebuilding a RAID 6 array after a disk failure can be time-consuming, as it involves reading data from all the remaining drives.
Understanding RAID 10
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a widely adopted RAID level that combines the advantages of disk mirroring and striping. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of RAID 10, its operation, and the benefits it offers.
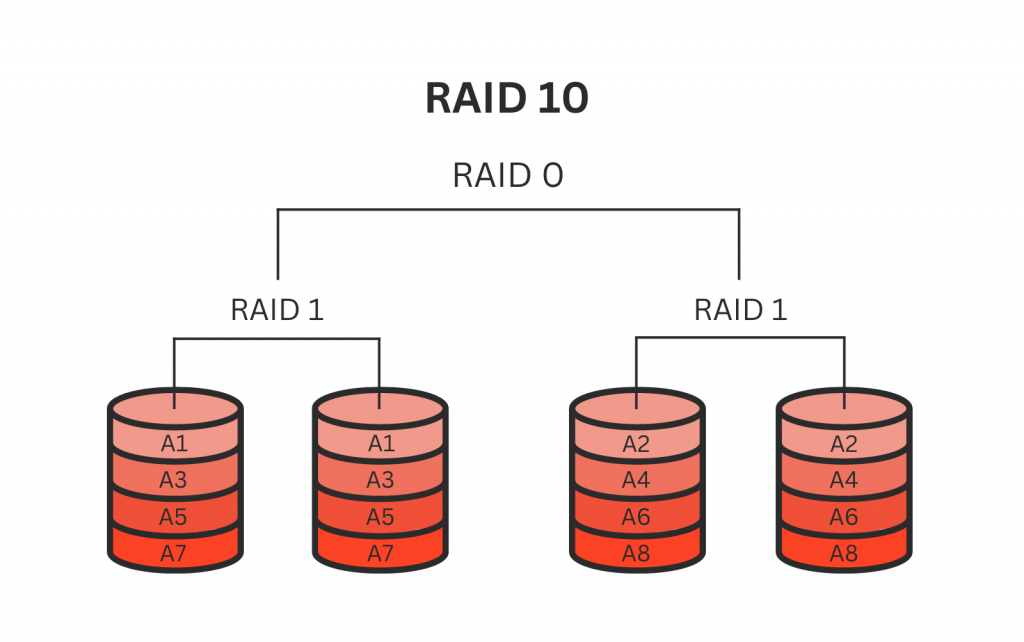
RAID 10 is a nested RAID configuration that combines the best features of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping). It requires a minimum of four drives and provides both data redundancy and improved performance. In RAID 10, data is simultaneously written to two sets of drives using disk mirroring. Each set is then striped together using RAID 0, which distributes the data across the drives. The result is a configuration that offers both data redundancy and enhanced performance.
Advantages of RAID 10
High Performance
RAID 10 offers excellent read and write performance, making it ideal for applications that require high-speed data access.
Fast Rebuild Times
Rebuilding a RAID 10 array is faster than rebuilding RAID 6 since it only involves copying data from the mirrored disk to a new replacement disk.
Improved Fault Tolerance
RAID 10 can sustain multiple disk failures as long as they don’t occur within the same mirrored pair.
Disadvantages of RAID 10
Disk Utilization
RAID 10 has a lower disk utilization compared to RAID 6. In RAID 10, only half of the total disk capacity is usable due to mirroring. This means that larger disk capacities may require more physical disks to achieve desired storage capacity.
Limited Scalability
RAID 10 is not easily scalable, as it requires adding mirrored pairs of disks. Expanding the array may involve rebuilding the entire system.
RAID 6 vs RAID 10
When comparing RAID 6 and RAID 10, it is important to consider several factors, including disk capacity, disk utilization, data loss prevention, and overall performance.
Disk Capacity and Utilization
RAID 6 utilizes disk capacity more efficiently compared to RAID 10. RAID 6 requires only two drives for parity, allowing for a higher usable storage space compared to RAID 10, which mirrors data and reduces the available capacity by half.
Data Loss Prevention
Both RAID 6 and RAID 10 provide robust data protection, but their approaches differ. RAID 6 can tolerate the simultaneous failure of up to two drives, thanks to its dual parity scheme. On the other hand, RAID 10 can withstand the failure of one drive in each mirrored set. In terms of data loss prevention, RAID 6 offers a higher level of fault tolerance.
Performance
When it comes to performance, RAID 10 takes the lead. The striping configuration of RAID 10 provides improved read and write speeds, making it ideal for applications that require high-performance data access. RAID 6, with its dual parity calculations, may have slightly slower write speeds compared to RAID 10.
Cost
In terms of cost, RAID 6 is generally more affordable than RAID 10. RAID 6 requires fewer drives for implementation, resulting in lower hardware costs. RAID 10, with its mirroring and striping configuration, requires more drives and can be more expensive.
Choosing between RAID 6 and RAID 10 depends on your specific requirements and priorities. RAID 6 offers efficient disk capacity utilization, high fault tolerance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for environments that prioritize storage efficiency and data protection. RAID 10, on the other hand, excels in performance, providing faster read and write speeds, and offers robust fault tolerance.

Consider factors such as your storage capacity needs, desired level of data protection, performance requirements, and budget constraints when making your decision. Whether you opt for RAID 6 or RAID 10, both RAID levels can provide reliable data protection, and understanding their differences will help you select the most appropriate solution for your specific storage environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between RAID 6 and RAID 10?
The main difference lies in their configurations. RAID 6 utilizes block-level striping with dual parity, offering high fault tolerance and efficient disk utilization. On the other hand, RAID 10 combines disk mirroring and striping, providing improved performance and fault tolerance.
Which RAID level is better for data protection?
Both RAID 6 and RAID 10 offer strong data protection capabilities, but they excel in different areas. RAID 6 can tolerate the failure of two drives simultaneously, making it highly resilient against data loss. RAID 10, on the other hand, provides faster rebuild times and excellent performance, ensuring quick recovery in case of disk failures.
Which RAID level is more cost-effective?
In terms of cost-effectiveness, RAID 6 is generally more affordable than RAID 10. RAID 6 requires fewer drives for implementation, resulting in lower hardware costs. RAID 10, with its mirroring and striping configuration, requires more drives and can be more expensive.
Which RAID level is better for maximizing storage capacity?
RAID 6 is better suited for maximizing storage capacity. It offers efficient disk utilization, allowing for larger usable storage space compared to other RAID levels. RAID 10, due to its mirroring approach, provides usable storage space equal to half the total disk capacity.
Which RAID level is recommended for high-performance applications?
RAID 10 is typically recommended for high-performance applications that require fast data access. Its striping configuration improves read and write speeds, allowing for improved performance. RAID 6, while offering robust data protection, may have slightly slower write speeds due to the dual parity calculations.
