In today’s digital age, where data is the lifeblood of businesses and individuals alike, safeguarding this precious resource is of paramount importance. This has led to the widespread adoption of various backup strategies to ensure that data loss does not translate into irreversible setbacks. Among these strategies, two prominent contenders stand out: full backup and incremental backup. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of these backup approaches, explore their benefits, and help you understand which one might be the best fit for your needs.
Understanding Full Backup
Full Backup, as the name suggests, involves creating a complete duplicate copy of all data and files within a system. This initial snapshot captures everything, from documents and images to applications and settings. The process typically starts with a full backup, which serves as the foundation for subsequent backup operations.
Unveiling Incremental Backup
Incremental Backup, on the other hand, is a more nuanced approach that focuses on efficiency. Instead of copying all the data every time a backup is performed, incremental backups only copy the data that has changed since the last backup, be it a full backup or an incremental backup. In essence, it adds only the new or modified data to the existing backup set, thus forming a chain of changes.
Full Backup vs. Incremental Backup
Choosing between these backup methods depends on factors such as data volume, recovery time objectives, and available resources. Let’s compare them across various aspects:
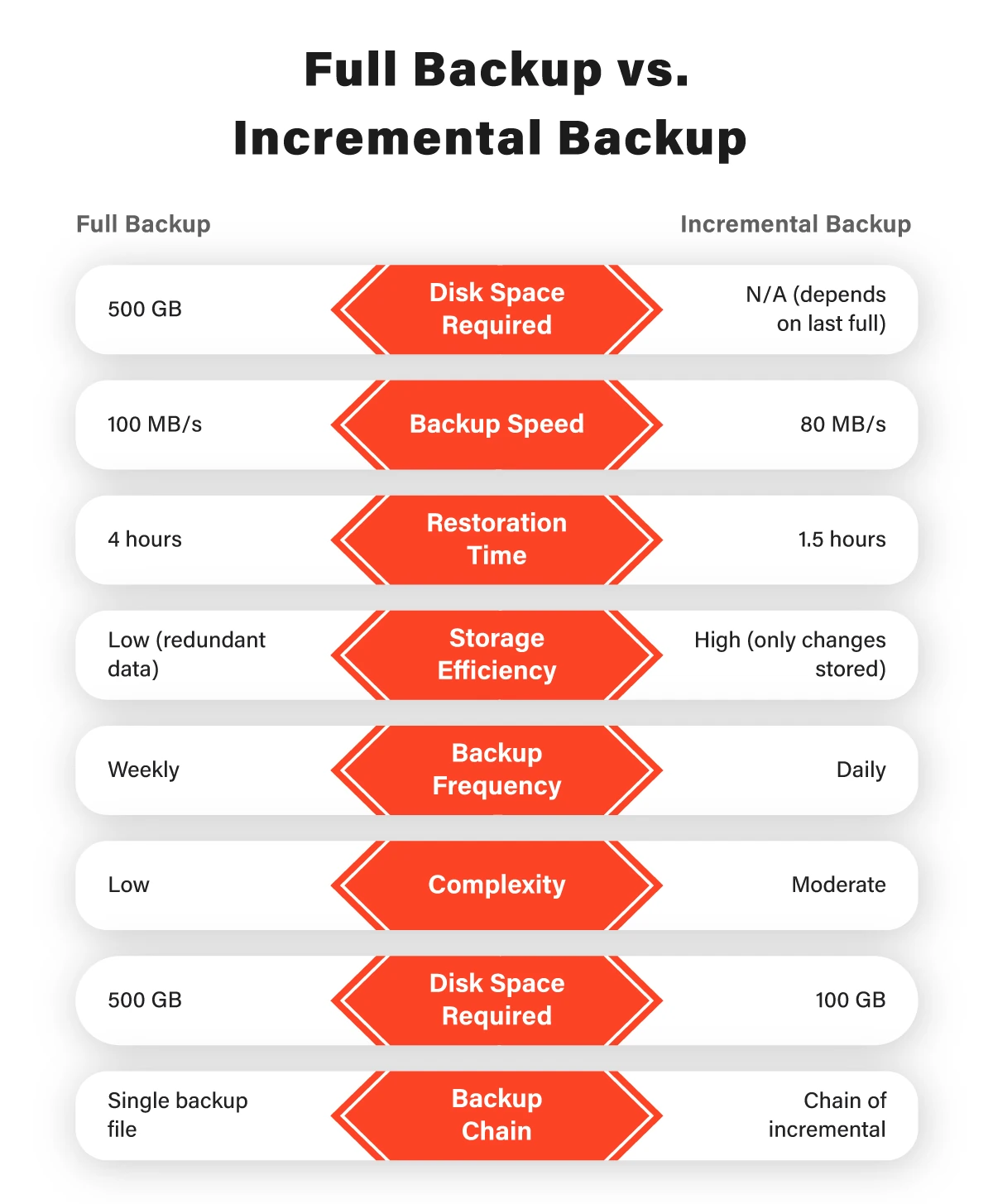
Backup Process
- Full Backup: Involves copying all data creating a complete snapshot of the system.
- Incremental Backup: Copies only the data that has changed since the last backup, forming a chain of incremental changes.
Backup Sets
- Full Backup: Generates standalone backup sets, simplifying restoration but potentially using more storage space.
- Incremental Backup: This creates a backup chain, where each incremental backup relies on the last full backup and subsequent incremental backups.
Storage Usage
- Full Backup: Requires more storage space due to duplicating all data with each backup.
- Incremental Backup: Consumes less storage space, as only changes are added.
Backup Speed
- Full Backup: Initial full backup can be time-consuming, and subsequent backups may also take a while.
- Incremental Backup: Generally faster, especially for routine backups, as only changes are copied.
Recovery Time
- Full Backup: Faster restoration due to all data being in one place.
- Incremental Backup: Recovery involves restoring the last full backup and applying the latest incremental changes, leading to faster recovery times.
Disaster Recovery
- Full Backup: Robust disaster recovery due to comprehensive data coverage.
- Incremental Backup: Reliant on maintaining a coherent backup chain; loss of any incremental backup can affect recovery.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the appropriate backup method depends on your specific needs and priorities. Here are some guiding questions:
- How critical is your data? If your data is highly sensitive and irreplaceable, a full backup might offer the most comprehensive protection.
- What are your storage limitations? If storage space is a concern, incremental backups could be a more efficient choice.
- What is your recovery time objective? If minimizing downtime is crucial, incremental backups might provide a faster path to recovery.
The battle between full backup and incremental backup continues to be a topic of discussion among IT professionals and data enthusiasts. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suited for different scenarios. Whether you opt for the comprehensive coverage of a full backup or the efficiency of incremental backups, the key lies in aligning your choice with your data protection needs. Remember, it is not a matter of one approach being universally superior; rather, it is about choosing the approach that best safeguards your data and supports your recovery goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a full backup?
A full backup is a comprehensive copy of all data and files in a system at a specific point in time. It captures everything, ensuring a complete snapshot of the dataset. However, it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for large amounts of data.
What is an incremental backup?
An incremental backup captures only the changes made since the last backup, be it a full backup or a previous incremental backup. It’s much faster and consumes less storage space compared to full backups. It creates a chain of backups, focusing only on modifications.
How does the incremental backup process work?
The incremental backup process starts with a full backup. After that, subsequent incremental backups copy only the new or modified data. Backup software analyzes file attributes to capture changes, making the process efficient and quicker over time.
Which one is faster: full backup or incremental backup?
Incremental backups are faster compared to full backups. This is because they only deal with changes since the last backup, whereas full backups copy all data. This speed advantage makes incremental backups a good choice for frequent backups.
