Understanding the key differences is crucial to making informed decisions regarding your computing needs. It involves grasping their working principles, speed performance, durability, noise levels, heat production, and overall cost. When choosing a storage drive for your computer system, you can choose from two primary types of drives: Solid State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). The drive type is the most fundamental difference between solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs). An SSD is a non-mechanical device that stores data on flash memory. These two types of drives differ in many ways, from the type of drive to the speed, performance, and reliability. This article will explore the key differences between SSDs and HDDs to help you make an informed decision.
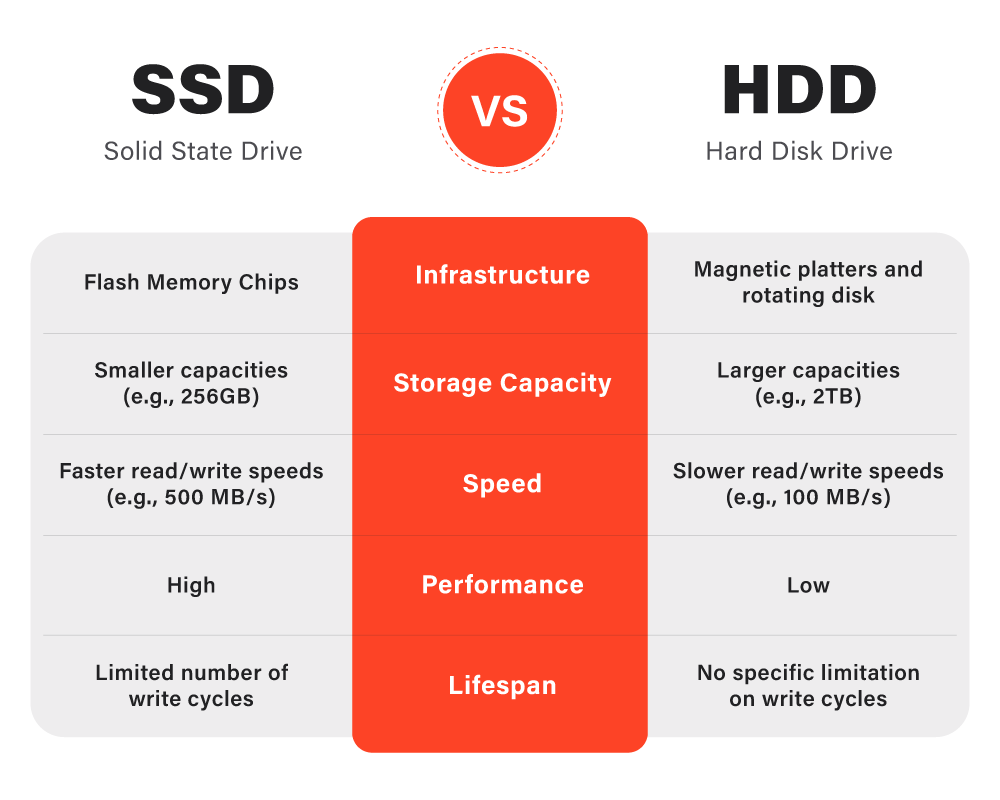
Infrastructure
HDD vs. SSD Infrastructure: HDD, standing for Hard Disk Drive, operates on magnetism, and it involves a mechanical arm moving over a spinning disk to read and write data. The moving parts of an HDD are responsible for reading and writing data from the spinning disks. The disks rotate at high speeds, and the read/write head moves across the platters to access the stored data. As the head moves across the disk, it creates a lot of heat and friction, leading to wear and tear over time. The actuator arm moves the read/write head, adding to the drive’s mechanical complexity. In contrast, SSDs use flash memory to store data.
Flash memory is a non-volatile memory that can retain data even when power is turned off. SSDs have no moving parts and rely on electrical circuits to access data stored on the drive. This design results in faster access times, less power consumption, and less susceptibility to damage due to shock or vibrations.
The lack of moving parts in SSDs also means that they produce less noise and heat than HDDs. This makes SSDs a better choice for laptops, as they help reduce heat buildup, leading to longer battery life and improved overall performance.
Storage Capacity
Storage capacity is crucial when choosing between an HDD and an SSD. HDDs have been the go-to option for many years due to their high storage capacity. With the ability to store up to several terabytes of data, they are ideal for storing large files such as high-resolution images, videos, and games. The larger capacity also makes them a popular choice for servers requiring vast storage space.
On the other hand, SSDs have traditionally been known for their limited storage capacity. However, with advancements in technology, their storage capacity has been increasing steadily over the years.
Currently, the highest capacity SSD available on the market is around 4TB, which is still significantly less than the maximum storage capacity of the hard drive. Nonetheless, the storage capacity of SSDs is often more than enough for the average user who does not require vast amounts of storage space.

It is worth noting that SSDs can be more expensive per storage unit than HDDs. Therefore, an HDD may be more cost-effective for users requiring vast storage space. However, an SSD is how users prioritize speed and reliability.
Speed and Performance
The difference in speed and performance between SSDs and HDDs is significant. Since SSDs do not have any mechanical components, they are much faster than HDDs. The lack of spinning platters and read/write heads makes SSDs faster at accessing and transferring data. In addition, SSDs have faster read and write speeds, meaning they can read and write data much more quickly than HDDs. This makes SSDs ideal for running applications and operating systems that require high speed and performance, such as gaming, video editing, and graphic design.

In contrast, HDDs have slower read and write speeds due to their mechanical components. The read/write head must physically move to the location of the data on the spinning platters, which can take time.
This can cause longer load times for applications and operating systems, which can be frustrating for users. However, due to their high storage capacity, HDDs are still useful for storing large files, such as videos and photos.
Wear and Tear - Solid-State Drive vs Hard Disk Drive
The lack of moving parts in SSDs improves their speed and performance and makes them more durable. Unlike HDDs, which use spinning disks and read/write heads to access data, SSDs use non-volatile flash memory. This means that SSDs are unaffected by mechanical failures, such as disk fragmentation or head crashes, that can occur in HDDs. Moreover, SSDs are not affected by environmental factors such as shock or vibration, making them ideal for portable devices such as laptops and tablets.
Additionally, SSDs have a longer lifespan than HDDs because they have no moving parts that can wear out over time. This means that SSDs can last for many years, even with frequent use. Overall, the absence of moving parts in SSDs makes them more reliable and less prone to failure than HDDs.
In conclusion, when it comes to choosing between an SSD and an HDD, it ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences. An SSD is the better option if you require high-speed performance and reliability. However, an HDD may be the right choice if you require high storage capacity and don’t mind slower read and write speeds. Ultimately, it comes down to your specific requirements and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between HDD and SSD?
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid-State Drive) are two types of storage devices with distinct technologies. HDDs use spinning disks (platters) and mechanical read/write heads to store and retrieve data, while SSDs utilize flash memory chips for data storage, which have no moving parts.
Which is faster, HDD or SSD?
SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs. The absence of moving parts allows SSDs to access and retrieve data almost instantly, resulting in faster boot times, application launches, and overall system responsiveness. HDDs, due to their mechanical nature, are slower in data access and transfer speeds.
Which is more durable, HDD or SSD?
SSDs are more durable than HDDs. Since SSDs do not have any moving parts, they are less susceptible to mechanical failure caused by drops, bumps, or vibrations. HDDs, on the other hand, have spinning platters and mechanical read/write heads that can be damaged if mishandled or exposed to physical shocks.
Which has a longer lifespan, HDD or SSD?
SSDs generally have a longer lifespan than HDDs. While both types of drives can last for many years, SSDs can endure a higher number of read/write cycles before they start to degrade. However, it’s important to note that the lifespan of an SSD also depends on factors like the quality of the flash memory and usage patterns.
Can I replace my HDD with an SSD?
Yes, in most cases, you can replace your HDD with an SSD. However, it is essential to ensure that your system supports the interface (e.g., SATA, NVMe) used by the SSD and that you have the necessary connectors and mounting options. You will also need to reinstall the operating system and transfer your data to the new SSD.
