In today’s digital age, where speed and efficiency are paramount, traditional disk drives (HDDs) are rapidly being replaced by solid-state drives (SSDs). Among SSDs, two popular options are SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs. These storage devices offer significant improvements in performance, reliability, and form factor over their mechanical counterparts. In this blog post, we will delve into the key differences between SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs, shedding light on their features, benefits, and use cases.
What is an SSD, and How Does It Work?
Before we explore SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs, let’s have a brief understanding of SSDs in general. Solid-state drives are storage devices that use flash memory to store and retrieve data, unlike HDDs that rely on spinning disks and mechanical read/write heads. SSDs are non-volatile memory devices, meaning they retain data even when the power is turned off.
SSDs utilize integrated circuits to store data in memory cells. Each cell can store multiple bits of information, and when electrical charges are applied, the cells can be programmed or erased. This flash memory technology allows SSDs to offer faster access times, lower latency, and improved durability compared to HDDs.
SSD Types: SATA and NVMe
SSDs come in various form factors and interfaces. Two common types are SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs, which differ in terms of their performance and compatibility.
What is SATA SSD?
Serial ATA (SATA) SSDs are the traditional choice for solid-state storage. They utilize the SATA interface, which has been widely adopted for connecting storage devices to computers.

SATA SSDs typically come in a 2.5-inch form factor, resembling the size of a laptop HDD, making them compatible with most desktop and laptop systems.
SATA SSDs offer significant performance advantages over HDDs, including faster data transfer rates, reduced access times, and improved reliability due to the absence of moving parts. However, SATA SSDs face limitations when it comes to their maximum potential speeds due to the constraints of the SATA interface.
What is NVMe SSD?
Non-volatile memory Express (NVMe) SSDs are the next generation of solid-state storage devices designed to leverage the full potential of flash memory technology. NVMe is an advanced host controller interface and storage protocol developed explicitly for PCIe SSDs. PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a high-speed interface commonly used for connecting peripheral devices, including graphics cards and network adapters.
NVMe SSDs, typically available in the M.2 form factor, provide unparalleled performance and scalability. The M.2 NVMe SSDs directly interface with the PCIe bus, allowing for much higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to SATA SSDs. This enables NVMe SSDs to deliver blazing-fast read and write speeds, making them ideal for demanding workloads such as gaming, content creation, and data-intensive applications.
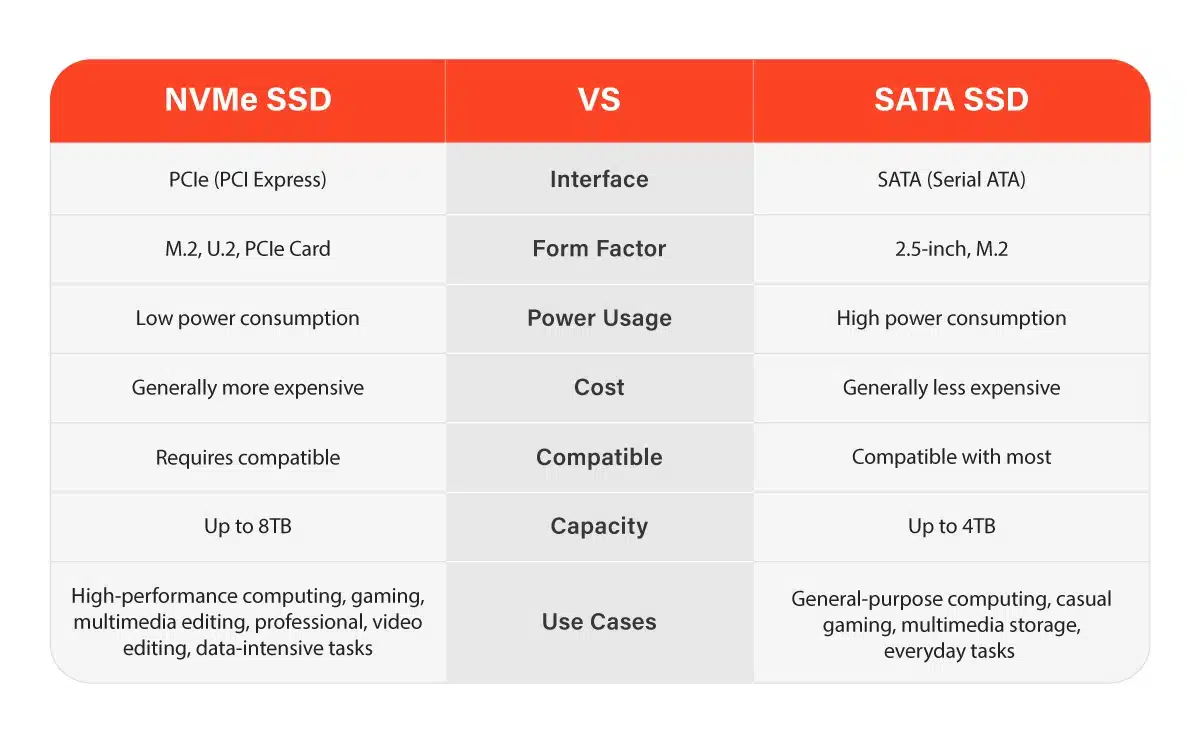
SATA SSD vs. NVMe SSD
When deciding between SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs, there are several factors to consider:
Performance
NVMe SSDs offer significantly higher performance compared to SATA SSDs. The PCIe interface used by NVMe drives provides a wider data pipeline, allowing for faster data transfer rates and lower latency. NVMe SSDs can achieve sequential read and write speeds of several gigabytes per second, while SATA SSDs typically operate at lower speeds. If you require maximum performance and have data-intensive workloads, NVMe SSDs are a clear choice.
Form Factor and Compatibility
SATA SSDs are available in the 2.5-inch form factor, making them compatible with most desktop and laptop systems. On the other hand, NVMe SSDs predominantly come in the M.2 form factor, which offers a smaller footprint and is well-suited for ultrabooks and compact desktop builds. It’s essential to ensure your system supports the M.2 interface before opting for an NVMe SSD.

Price
SATA SSDs are generally more affordable compared to NVMe SSDs. As NVMe technology continues to evolve, prices are gradually decreasing, but SATA SSDs still provide better value for budget-conscious consumers. If you are primarily concerned with cost and do not require the absolute highest performance, a SATA SSD is a cost-effective choice.
Use Cases
SATA SSDs are suitable for a wide range of applications, including operating system installations, general computing tasks, and everyday use. They offer a substantial upgrade over HDDs and provide a noticeable boost in overall system responsiveness.

NVMe SSDs shine in scenarios where ultra-fast storage performance is crucial.
Gamers, content creators, and professionals working with large datasets or complex simulations can benefit greatly from the exceptional read and write speeds offered by NVMe SSDs.
They excel in tasks that involve heavy multitasking, large file transfers, and high-end gaming.
When it comes to choosing between SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs, it depends on your specific needs and budget. SATA SSDs are reliable, cost-effective, and significantly improve performance over traditional HDDs. NVMe SSDs, on the other hand, offer unparalleled speed and are ideal for power users and professionals who require maximum performance.
As NVMe technology continues to advance and prices become more competitive, it’s likely that we will see wider adoption of NVMe SSDs in various computing devices. Ultimately, the decision between SATA and NVMe comes down to finding the right balance between performance, cost, and compatibility for your specific use case.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between SATA SSD and NVMe SSD?
The main difference lies in the interface they use to connect to the system. SATA SSDs use the SATA interface, while NVMe SSDs utilize the PCIe interface. This distinction significantly impacts their performance capabilities.
Which one is faster: SATA SSD or NVMe SSD?
NVMe SSDs are generally faster than SATA SSDs due to the higher bandwidth and lower latency provided by the PCIe interface. NVMe SSDs can achieve much higher sequential read and write speeds, resulting in improved overall performance.
Are SATA SSDs compatible with systems that support NVMe?
Yes, SATA SSDs are compatible with systems that support NVMe. However, it’s important to note that NVMe systems may not fully utilize the potential speed of SATA SSDs. It’s advisable to check the compatibility and available interfaces of your system before making a purchase.
Can I use an NVMe SSD in a system that supports SATA SSDs?
In most cases, yes. NVMe SSDs can be used in systems that have a compatible M.2 slot or a PCIe adapter. However, it’s crucial to verify the compatibility of your system before installing an NVMe SSD.
Which type of SSD is better for gaming?
For gaming, NVMe SSDs are generally the preferred choice. Their faster read and write speeds allow for quicker game loading times and improved in-game performance. However, it’s worth noting that the difference in gaming experience between SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs may not be substantial for the average gamer.
