In the ever-evolving landscape of data storage solutions, Solid State Drives (SSDs) have revolutionized the way we handle data. Unlike traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), SSDs boast incredible speed, efficiency, and reliability, owing to their lack of moving parts and reliance on flash memory technology. Among SSDs, two prominent contenders vie for supremacy: SAS SSD and SATA SSD. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between these two technologies, examining their benefits, performance, and applications to help you make an informed decision when choosing the right SSD for your needs.
Understanding SSD Technology
Before diving into the specifics of SAS SSD and SATA SSD, let’s take a moment to understand the basics of SSD technology. Unlike HDDs, which utilize magnetic platters and read/write heads, SSDs leverage NAND flash memory to store and access data. This fundamental difference eliminates the need for moving parts, making SSDs more durable, shock-resistant, and power-efficient. The lack of mechanical components also translates to quicker access times, improved random read/write speeds, and reduced latency.
SATA SSD: High Performance Meets Affordability
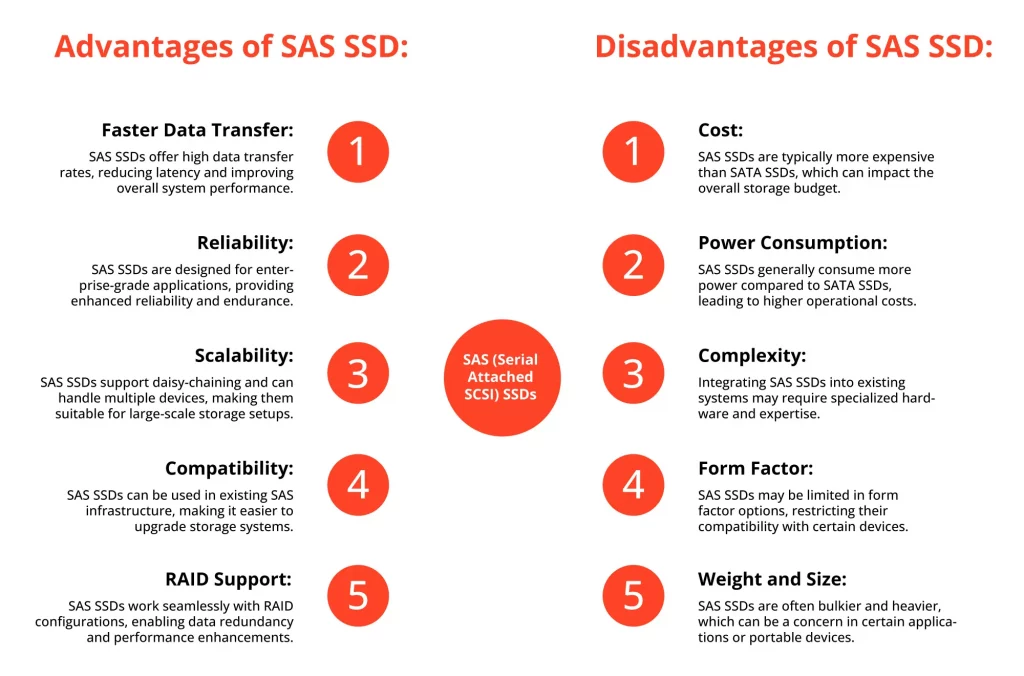
SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) SSDs, on the other hand, take SSD performance to a whole new level. SAS is a high-speed, high-performance interface designed for enterprise-level applications. SAS SSDs have faster data transfer rates and more robust data handling capabilities compared to SATA SSDs. They are particularly well-suited for tasks that require lightning-fast read/write speeds and low latency, such as real-time data processing, database applications, and virtualization environments.

The key difference between SAS and SATA lies in their architectures. While SATA SSDs are typically designed for client applications, SAS SSDs are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of enterprise-level workloads. SAS SSDs often come equipped with better error correction, enhanced power loss protection, and superior end-to-end data integrity, making them more reliable than SATA drives in critical business environments.
Performance Comparison: SAS SSD vs. SATA SSD
When comparing SAS SSD and SATA SSD performance, the differences become evident. SAS SSDs have higher read/write speeds, which can reach up to several gigabytes per second, while SATA SSDs generally achieve speeds in the hundreds of megabytes per second range. For sequential workloads or transferring large files, SAS SSDs significantly outpace SATA SSDs.
In terms of random I/O performance, SAS SSDs also maintain a clear advantage. The advanced SAS interface allows for a higher number of input/output operations per second (IOPS), making them ideal for tasks that involve numerous small read/write operations simultaneously.

Application Scenarios: SAS, SATA, and NVMe
The choice between SAS, SATA, and NVMe SSDs largely depends on the intended use case and budget constraints.
- SATA SSDs: These drives are best suited for everyday computing tasks, such as web browsing, document editing, and multimedia consumption. They offer a cost-effective solution for individuals and small businesses looking to upgrade from traditional HDDs without breaking the bank.
- SAS SSDs: Enterprises and data centers benefit the most from SAS SSDs, which excel in high-performance computing environments. They are well-suited for hosting virtual machines, handling large-scale databases, and running mission-critical applications.
- NVMe SSDs: NVMe drives represent the pinnacle of SSD technology, offering even faster speeds than both SAS and SATA. These drives are ideal for workloads that demand extreme performance, such as content creation, high-resolution video editing, and complex simulations.

Reliability: SAS SSDs Take the Lead
Reliability is a critical factor when choosing storage solutions for important data. SAS SSDs, with their enterprise-grade design, are inherently more reliable than SATA drives. The superior error correction capabilities and enhanced data integrity mechanisms of SAS SSDs ensure that data is consistently protected and maintained.
While SATA SSDs are undoubtedly more reliable than traditional HDDs, they may not provide the level of robustness required for mission-critical applications. For this reason, SAS SSDs are the preferred choice in scenarios where data loss or system failure could have severe consequences.
In the SSD world, both SAS SSD and SATA SSD have their strengths and weaknesses. SATA SSDs offer an affordable entry point into the world of solid-state storage, providing a significant performance boost over traditional HDDs. On the other hand, SAS SSDs unleash the true potential of SSD technology with their high-speed interface, impressive read/write speeds, and enterprise-level reliability.
When deciding between SAS SSD and SATA SSD, consider the nature of your workload, the level of performance required, and the importance of data integrity. For everyday computing tasks, SATA SSDs are more than sufficient. However, if your business relies on high-performance computing or mission-critical applications, investing in SAS SSDs will be a wise decision that ensures optimal performance and data safety.
Ultimately, regardless of your choice, embracing the world of solid-state drives marks a significant step toward a faster, more reliable, and more efficient computing experience. As technology continues to evolve, SSDs will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of data storage solutions, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the digital realm.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between SAS SSD and SATA SSD?
SAS SSD and SATA SSD differ primarily in their interface and intended use. SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) SSDs are designed for high-performance enterprise applications, providing faster data transfer rates and greater reliability. SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) SSDs, on the other hand, are commonly used in consumer-grade devices and entry-level servers, offering a more cost-effective solution for everyday computing tasks.
Which SSD is faster, SAS or SATA?
SAS SSDs are generally faster than SATA SSDs. With their high-speed interface and advanced data handling capabilities, SAS SSDs achieve higher read/write speeds, making them ideal for tasks that require lightning-fast data access, such as database applications and real-time data processing.
Can I use a SAS SSD in my personal computer or laptop?
SAS SSDs are compatible with some systems, but they are not a standard option for personal computers or laptops. SAS interfaces are mainly found in enterprise-grade servers and data center equipment. For consumer-grade devices, SATA SSDs are the more common and suitable choice.
Are SAS SSDs more reliable than SATA SSDs?
Yes, SAS SSDs are generally considered more reliable than SATA SSDs. SAS SSDs are built for enterprise-level use and come equipped with enhanced error correction, power loss protection, and end-to-end data integrity mechanisms. These features make SAS SSDs better suited for critical business environments where data reliability is paramount.
Are there any cost differences between SAS SSD and SATA SSD?
Yes, there is a cost difference between SAS SSD and SATA SSD. SAS SSDs are typically more expensive than SATA SSDs due to their advanced technology and enterprise-grade features. SATA SSDs provide a more budget-friendly option for those seeking faster storage performance without the premium price tag associated with SAS SSDs.
