In the complicated data storage and redundancy world, RAID 1 is a heroic defender against the looming threat of data loss. However, even the most powerful systems can encounter challenges, and one such challenging enemy is the specter of drive failure within a RAID 1 array. This guide delves into the nuances of RAID 1 drive failure – from understanding the potential causes to recognizing warning signs and, crucially, the meticulous steps involved in rebuilding RAID 1 after a drive failure.
As we navigate through the sophistication of this recovery process, we’ll shine a spotlight on PITS GLOBAL Data Recovery Services, a trusted ally in the realm of RAID failures, offering specialized expertise and solutions to salvage precious data from the brink of loss.
RAID 1 Drive Failure
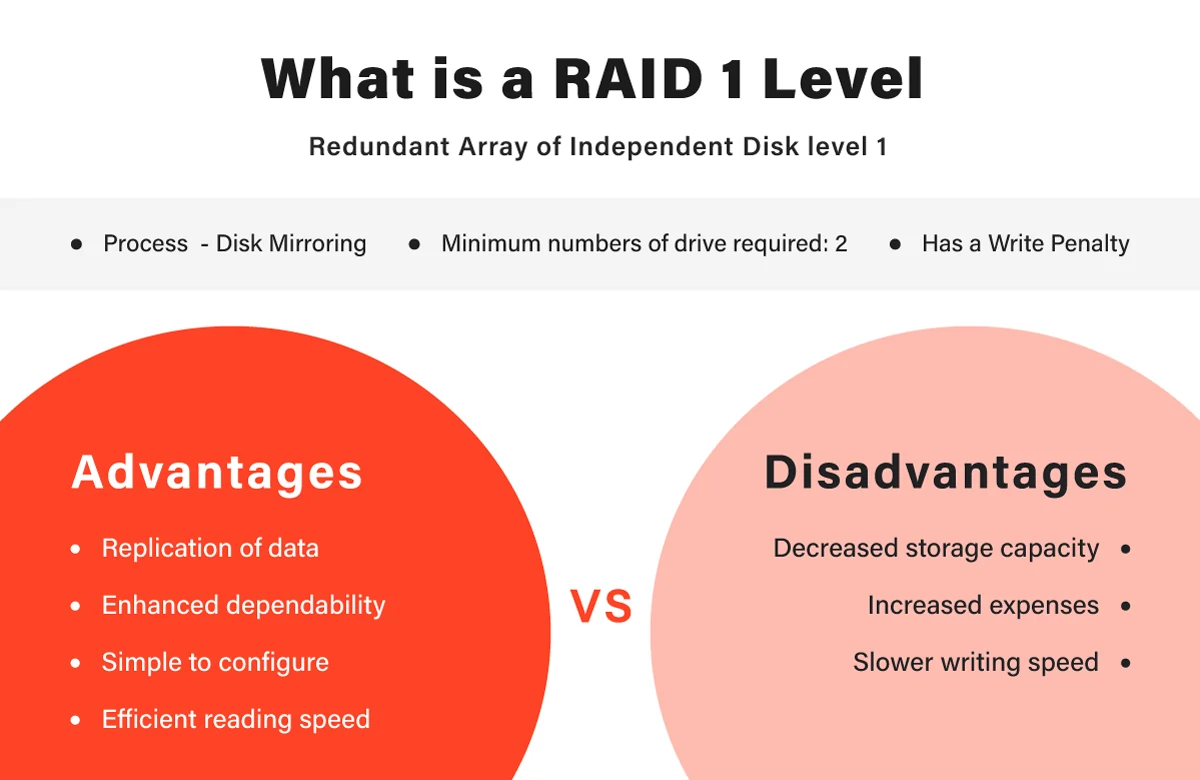
RAID 1, or mirroring, is a data storage configuration that duplicates information across two or more hard drives, creating an identical copy, or mirror, of the data. This mirroring concept ensures that if one drive fails, the system can seamlessly switch to the mirrored drive, preventing data loss and minimizing downtime. The beauty of RAID 1 lies in its ability to provide redundancy, offering a safety net against the unpredictable nature of hardware failures.
Causes of Hard Drive Failure in RAID 1
Despite RAID 1’s robust design, hard drive failures can still occur. Understanding the potential causes is crucial for preemptive measures. Common factors contributing to RAID 1 drive failure include mechanical issues such as disk platter damage, electronic failures, overheating, and human error during maintenance or upgrades. By identifying these factors, administrators can take proactive steps to mitigate risks and ensure the continued reliability of their RAID 1 array.
Recognizing Signs of RAID 1 Hard Drive Failure
Spotting the early warning signs of a failing drive within your RAID 1 array can prevent data loss. Watch out for subtle cues like slower-than-usual performance, unexplained crashes, or unusual noises emanating from the hardware. These red flags might indicate an underlying issue that, if addressed promptly, can avert a full-blown drive failure.
Importance of Proactive Monitoring and Regular Checks
Caution is the key to maintaining a healthy RAID 1 system. Regularly monitoring the performance metrics and conducting routine checks on the status of individual drives can uncover potential problems before they escalate. Proactive measures such as these not only enhance the overall reliability of the RAID 1 array but also offer administrators the opportunity to take corrective action promptly.
"*" indicates required fields
Steps to Recover from RAID 1 Drive Failure
Facing a RAID 1 drive failure can be a daunting experience, but a systematic recovery approach can help reclaim valuable data. Before diving into the steps, assessing the situation calmly is essential. Begin by identifying the failed drive, a critical first step that sets the stage for subsequent actions.
Once the troubled drive is identified, the next move involves isolating it from the RAID array to prevent further complications. With these preliminary measures in place, the focus then shifts to implementing practical data recovery methods tailored to the unique circumstances of the RAID 1 drive failure.
1. Initial Assessment and Identification of the Failed Drive
Begin the recovery process by thoroughly assessing the RAID 1 array. Identify the specific drive that has encountered failure. This initial step lays the foundation for targeted actions in the subsequent recovery stages.
2. Isolating the Failed Drive from the RAID Array
Once the problematic drive is pinpointed, isolate it from the RAID array. This involves physically or logically disconnecting the failed drive to prevent any potential data corruption or interference with the recovery efforts.
3. Data Recovery Methods for RAID 1 Drive Failure
Implementing effective data recovery methods is crucial. Depending on the nature of the failure, these methods may include rebuilding the RAID array using a replacement drive, restoring data from backups, or requesting specialized data recovery services. Tailor the approach to the specific circumstances to maximize the chances of a successful recovery.
Rebuilding RAID 1 After Drive Failure
Recovering from a RAID 1 drive failure involves a meticulous process to restore data integrity and redundancy. Follow these straightforward steps to rebuild your RAID 1 array:
1. Identify the Failed Drive
The first crucial step in the recovery process involves a thorough assessment to identify the failed drive within the RAID 1 array. Administrators must scrutinize system logs, error messages, and RAID management tools to pinpoint the specific drive that has encountered issues. This initial assessment sets the stage for a targeted and efficient recovery strategy.
- Determine which drive in your RAID 1 setup has encountered failure through system logs or monitoring tools.
2. Replace the Failed Drive
Once the problematic drive is identified, proceed to isolate it from the RAID 1 array. This involves disconnecting or physically removing the failed drive to prevent potential data corruption or conflicts within the array. By isolating the malfunctioning component, the RAID 1 array can continue operating with the remaining healthy drive while preparations are made for recovery.
- Power down the system and replace the failed drive with a new, compatible one. Ensure it has a similar or larger capacity than the remaining drives.

3. Access RAID Configuration Utility
Boot the system and access the RAID configuration utility during the startup process. This is usually done by pressing a specific key (e.g., Ctrl+I for Intel RAID) as prompted.
4. Rebuild the RAID Array
- Within the RAID configuration utility, locate the option to rebuild the array. Select the new drive as the replacement for the failed one.
5. Monitor Rebuilding Process
- Allow the RAID controller to initiate the rebuilding process. It can take some time, depending on the size of your RAID 1 array and the speed of your drives. Monitor the progress through the RAID management interface.
6. Verify Rebuild Completion
- Once the rebuilding process is complete, verify the status of the RAID array. Ensure that the system recognizes the new drive and that the RAID array is healthy.
7. Perform System Checks
- Conduct thorough system checks to ensure the overall stability and performance of the RAID 1 configuration. Look out for any anomalies and address them promptly.
8. Update Backup
- As a precautionary measure, update your backup after successfully rebuilding the RAID 1 array. This ensures that your data remains safeguarded in case of any unforeseen issues.
By following these step-by-step instructions, you can effectively rebuild your RAID 1 array after a drive failure, restoring the redundancy and data protection that RAID 1 is designed to provide.
Benefits of Our Services
PITS Global distinguishes itself through advanced technology, industry experience, and a commitment to client satisfaction. The company employs cutting-edge tools and methodologies specifically tailored for RAID 1 recovery, ensuring a swift and secure retrieval of your valuable data. With a focus on transparency and personalized service, PITS Global has become the go-to choice for those seeking a reliable solution to RAID 1 drive failures.
Success Stories and Testimonials from Satisfied Clients
The true measure of any data recovery service lies in its clients’ success stories and testimonials. PITS GLOBAL takes pride in a portfolio of satisfied customers who have experienced seamless recoveries, even in the face of complex RAID failures. Real-world examples and client testimonials testify to PITS GLOBAL’s proficiency in navigating the challenges of RAID 1 data recovery, instilling confidence in those considering their services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAID 1?
RAID 1, also known as mirroring, is a data storage configuration that duplicates information across two or more hard drives. This mirroring concept ensures that if one drive fails, the system can seamlessly switch to the mirrored drive, preventing data loss and minimizing downtime.
What are common indicators of a failing drive in RAID 1?
Signs of a failing drive in RAID 1 include slower-than-usual performance, unexplained crashes, or unusual noises emanating from the hardware. Recognizing these early warning signs is crucial to preventing data loss.
What steps should be taken to recover from RAID 1 drive failure?
The recovery process involves an initial assessment to identify the failed drive, isolating the failed drive from the RAID array to prevent further issues, and then employing data recovery methods such as specialized data recovery software tools and professional services.
Why choose PITS GLOBAL for RAID 1 recovery?
PITS GLOBAL Data Recovery Services specializes in RAID failures, offering advanced technology, industry experience, and a commitment to client satisfaction. The company’s proficiency in RAID 1 recovery and transparent and personalized service make it a reliable choice for data recovery needs.
Can RAID 1 cause hard drive failure?
No, RAID 1 itself does not cause hard drive failure. RAID 1 is designed to prevent data loss by mirroring information across multiple drives. However, individual drives within the RAID array may still experience failures due to various factors such as mechanical issues, electronic failures, overheating, or human error during maintenance or upgrades.
