In the world of data storage, maintaining the integrity and availability of data is of utmost importance. This is where RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations come into play. RAID combines multiple hard drives into a single logical unit, providing fault tolerance and improving performance.
One such configuration is RAID 50, which strikes a balance between performance and data protection. In this beginner’s guide, we will delve into RAID 50, understand its workings, explore its advantages and disadvantages, and discover data recovery options with PITS.
Understanding RAID 50
RAID 50 is a nested RAID configuration that combines the features of RAID 5 and RAID 0. RAID 5 provides fault tolerance by distributing parity across multiple drives, while RAID 0 enhances performance through block-level striping. By merging these two configurations, RAID 50 aims to offer both data protection and improved performance.
In a RAID 50 configuration, multiple RAID 5 arrays are combined using RAID 0 striping. Here is a breakdown of the process:
- The drives are divided into multiple RAID 5 arrays, with each array consisting of a minimum of three drives. RAID 5 distributes parity information across the drives in the array, providing fault tolerance in case of a single drive failure.
- RAID 0 striping is then applied across these RAID 5 arrays. This involves dividing data into blocks and distributing them across the drives in each RAID 5 array. As a result, data is striped across multiple drives, enhancing performance during read and write operations.

By leveraging the strengths of RAID 5 and RAID 0, RAID 50 offers a balanced solution for data storage, providing both data protection and improved performance.
Advantages of RAID 50
- Fault tolerance: RAID 50 offers fault tolerance by distributing parity across multiple drives. In the event of a drive failure, data can be reconstructed using the parity information stored on other drives within the RAID set. This ensures that data remains accessible even when a drive fails.
- Improved performance: With RAID 50, data is striped across multiple drives, allowing for parallel access and increased throughput. This results in enhanced read and write performance, making RAID 50 suitable for applications that demand high-speed data transfer.
- Scalability: RAID 50 can be easily scaled by adding additional RAID 5 arrays to the configuration. This flexibility allows for increased storage capacity and performance as the need arises.
- Data storage efficiency: RAID 50 maximizes storage capacity utilization by combining the benefits of RAID 5 and RAID 0. It achieves fault tolerance with distributed parity while maximizing performance with striping.
Disadvantages of RAID 50
- Minimum drive requirement: RAID 50 requires a minimum of six drives to function properly. It needs a minimum of three drives per RAID 5 array and at least two RAID 5 arrays for RAID 0 striping. This can increase the initial cost of implementing RAID 50.
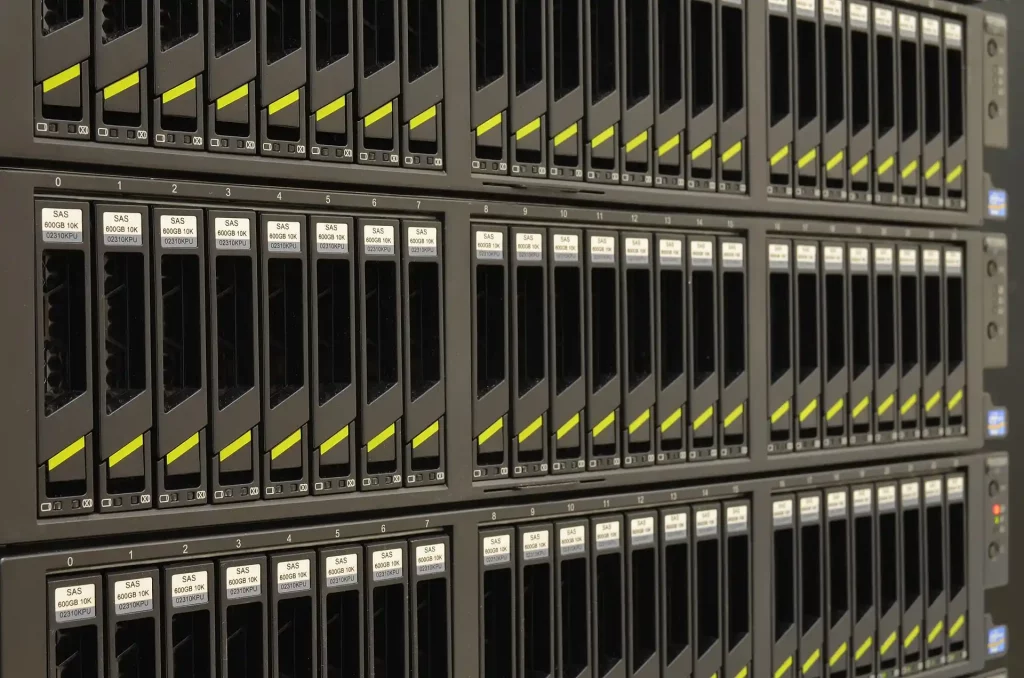

- Complexity: Compared to simpler RAID configurations, RAID 50 is relatively complex to set up and manage. It requires careful planning, configuration, and monitoring to ensure optimal performance and data protection.
- Data loss on RAID 50: While RAID 50 provides fault tolerance, it is not impervious to data loss. Multiple drive failures or catastrophic events can still lead to data loss, requiring appropriate data recovery measures.
Data Loss on RAID 50
While RAID 50 offers fault tolerance and data protection, it is not immune to data loss. Various factors can contribute to data loss on RAID 50 arrays. It is essential to be aware of these factors and take appropriate measures to mitigate the risks. Let’s explore some common scenarios where data loss can occur in RAID 50 configurations:
It is important to note that while RAID 50 provides fault tolerance, it is not a substitute for regular data backups. RAID should be considered as one layer of data protection, and backup solutions should be implemented to safeguard against any catastrophic data loss scenarios.
Services for RAID 50 at PITS Global
When data loss occurs in a RAID 50 configuration, seeking professional data recovery services becomes imperative. PITS specializes in RAID data recovery and possesses the expertise, tools, and techniques required to recover data from failed RAID 50 arrays.
PITS employs advanced data recovery methods, including specialized hardware and software, to recover data from damaged or inaccessible RAID 50 arrays. We have experience in dealing with various scenarios, such as RAID controller failures, multiple drive failures, and logical corruption. PITS ensures that your valuable data is recovered safely and efficiently, minimizing downtime and potential losses.

If you’re facing a data loss situation, don’t hesitate to contact us. Our 24/7 data recovery services are available to you, 365 days a year. Let us help you recover your precious data today.

We start the recovery process with a risk-free evaluation. Our technicians estimate reasons for data loss and the level of damage. Based on it, we select the most suitable recovery strategy.

With years in the data recovery industry, our company supports the highest customer satisfaction rate. We do everything to provide a positive experience for our clients.
During our remote customer file verification session, you will thoroughly review all necessary documents and records to ensure accuracy and compliance.
We offer data recovery services from over 50 locations across the US. This means that no matter where you are located, you can access our services to recover the data.
With our certified data recovery services and 99% success rate, we are confident that we can recover your precious data and get you back up and running in no time.
In conclusion, RAID 50 is a powerful data storage configuration that combines the fault tolerance of RAID 5 with the performance benefits of RAID 0. It offers data protection, improved performance, and scalability, making it suitable for various applications. While RAID 50 has its advantages and disadvantages, with proper planning, monitoring, and data recovery measures like those provided by PITS, the benefits can outweigh the drawbacks, ensuring reliable and robust data storage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAID?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a technology that combines multiple physical hard drives into a single logical unit to improve data storage performance, fault tolerance, and data protection.
What are the advantages of RAID 10?
RAID 10 offers excellent performance due to its striping capabilities and redundancy through mirroring. It provides high read and write speeds, making it suitable for applications that require high I/O operations. RAID 10 also provides better data protection as it can withstand multiple drive failures without data loss.
What is RAID 50?
RAID 50 is a nested RAID configuration that combines the features of RAID 5 and RAID 0. It provides both data protection and improved performance by striping data across multiple RAID 5 arrays.
How does RAID 50 work?
In RAID 50, multiple RAID 5 arrays are created, each requiring a minimum of three drives. The data is distributed across the drives within each RAID 5 array using distributed parity. Then, RAID 0 striping is applied across the RAID 5 arrays, enhancing performance by allowing parallel access to data.
Are there any disadvantages to RAID 50?
One disadvantage of RAID 50 is its minimum drive requirement. It needs a minimum of six drives to function properly, which can increase the initial cost. RAID 50 also involves more complexity in setup and management compared to simpler RAID configurations. Careful planning and monitoring are necessary for optimal performance and data protection.
