Backing up important data is essential for any organization or individual to ensure that the data can be recovered without much hassle in the event of a disaster. But choosing the right backup strategy can be tricky. Two of the most popular backup methods are incremental backup and differential backup.
In this blog, our team will explore these two strategies, their differences, and which one to choose for your specific needs.
What is Incremental Backup?
Incremental backup is a backup strategy that only copies the changes made to a file since the last backup. In other words, it only backs up the data modified or created since the last backup occurred. This means that incremental backup takes less time to complete and requires less storage space as compared to other backup strategies.
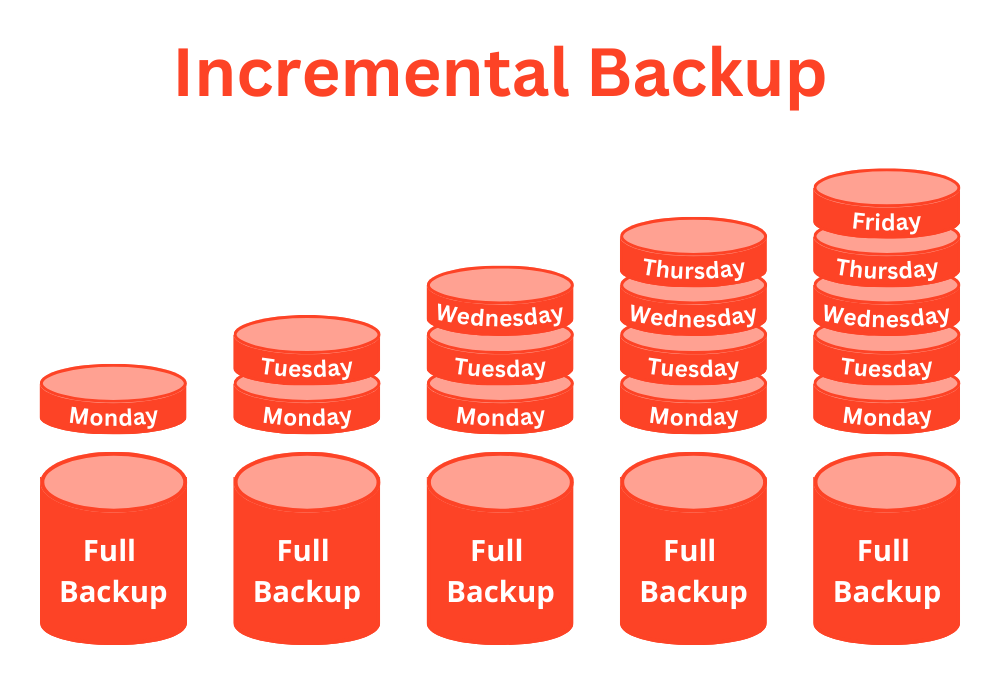
To understand incremental backup better, let us consider an example. Suppose you have a file called “document.docx” that you backed up on Monday. On Tuesday, you made some changes to the file and saved it.
Now, if you take an incremental backup on Tuesday, only the changes made to the file on Tuesday will be backed up. The previous backup taken on Monday will already have the data from the original file that was backed up. Therefore, the incremental backup will only add the new changes made to the file.
What is Differential Backup?
Differential backup is a backup strategy that backs up all the changes made to a file since the last full backup. In other words, it backs up all the data that has been modified or created since the last full backup was taken. This means that differential backup takes more time to complete and requires more storage space as compared to incremental backup.
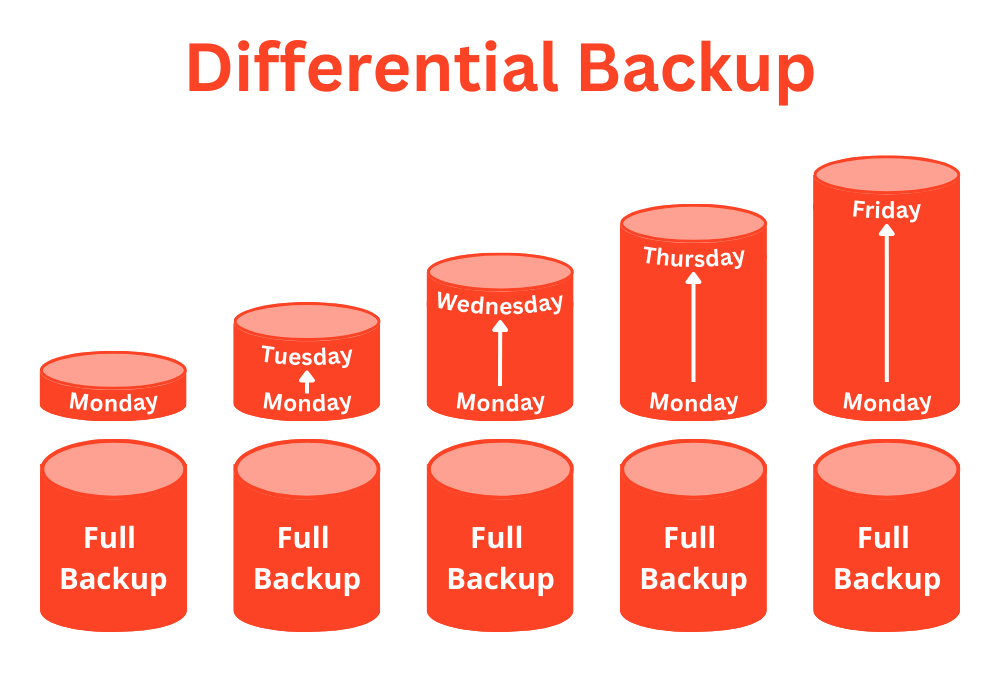
To understand differential backup better, let us consider the same example we used earlier. Suppose you have a file called “document.docx” that you backed up on Monday. On Tuesday, you made some changes to the file and saved it.
If you take a differential backup on Tuesday, it will back up all the changes made to the file since the last full backup was taken on Monday. This means that the Differential Backup will include all the changes made to the file on Monday as well as the changes made to the file on Tuesday.
Incremental vs. Differential Backup - Main Difference
The main difference between incremental backup and differential is the amount of data that is backed up. Incremental backup only backs up the changes made since the last backup, while differential backup backs up all the changes made since the previous full backup. This means that incremental backup requires less storage space and takes less time than differential backup.
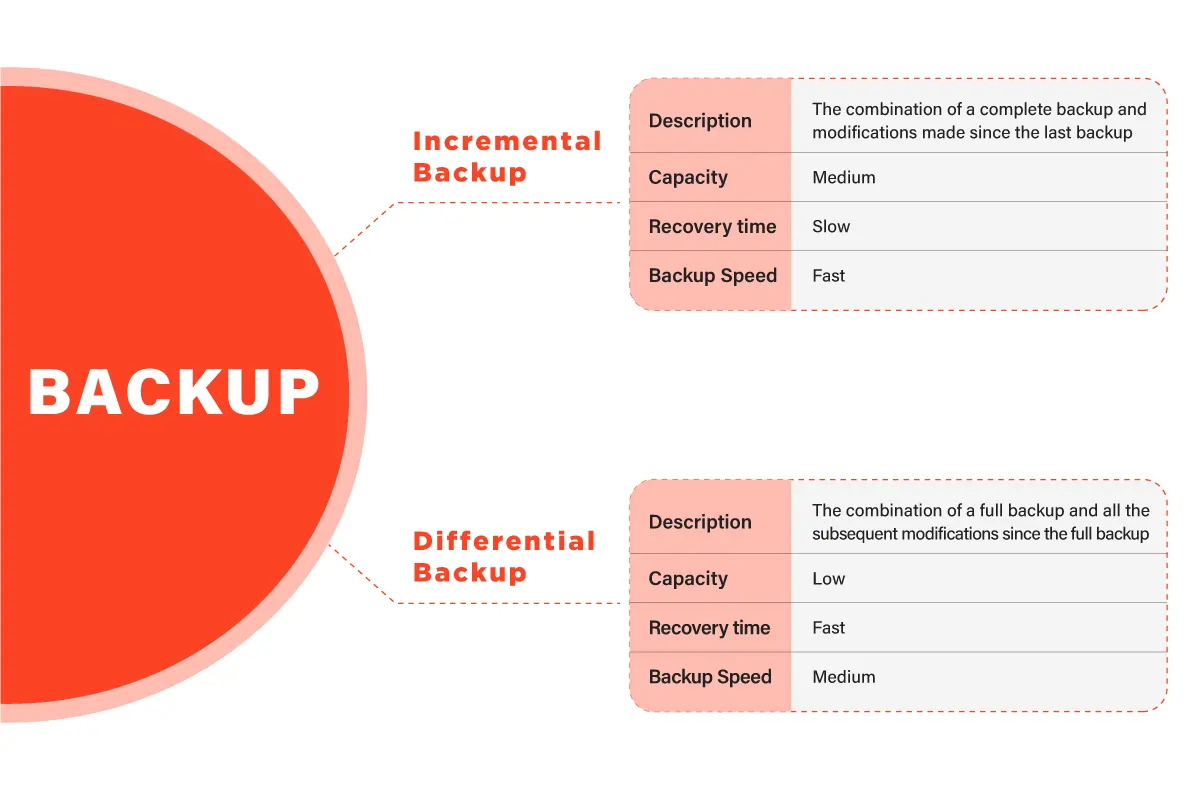
Another difference between incremental and differential backup is the recovery process. If you need to restore data from an incremental backup, you will need to retrieve the last full copy, and all the subsequent incremental ones are taken since then. This means that the disaster recovery process can be time-consuming and complicated, especially if you have a lot of incremental backups.
On the other hand, if you have to restore data from a differential backup, you will only need to retrieve the last full backup and the last differential backup taken since then. This means that the recovery process is much simpler, and recovery time is shorter for incremental backup.
Which One to Choose? - Differential vs. Incremental Backup
The choice between incremental backup and differential backup depends on your specific needs. If you have limited storage space and need to complete the backup process quickly, an incremental backup is a way to go. However, differential backup is a better choice if you have enough storage space and can afford to spend more time on the backup process.
Another factor to consider is the recovery process. If you need to restore data frequently, differential backup is a better choice as the recovery process is faster and simpler than incremental. However, if you do not need to retrieve data often, incremental backup can be a good choice as it takes less storage space and quickly completes the backup process.

It is worth noting that both incremental backup and differential backup have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice between the two backup strategies ultimately depends on your specific needs and requirements.
It is also important to consider other backup strategies, such as full backup, which backs up all data on a system, and hybrid backup, which combines the benefits of both incremental and differential backup.
In conclusion, incremental and differential backup are popular backup strategies that differ in the amount of data they back up and the recovery process. An incremental backup backs up only the changes made since the last backup, while differential backs up all changes made since the previous full backup.
The choice between the two types of backup ultimately depends on your specific needs and requirements, such as the amount of storage space available and the frequency of data restores. It is also important to consider other backup strategies to ensure that you choose the best backup strategy for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between incremental and differential backups?
Incremental Backup: An incremental backup only backs up data that has changed or been created since the last backup, whether it’s a full backup or a previous incremental backup. This method typically results in smaller backup sizes but requires more backup files for a complete restore.
Differential Backup: A differential backup backs up all the data that has changed or been created since the last full backup. It does not take into account previous differential backups. While the backup size increases over time, it requires fewer backup files for a complete restore compared to incremental backups.
Which backup method is more efficient in terms of storage space?
Incremental backups are generally more storage-efficient because they only back up changed or new data since the last backup. However, as time goes on, the number of incremental backups can accumulate and potentially occupy more storage space than differential backups.
Which backup method is faster to perform?
Incremental backups are usually faster to perform than full backups because they only involve copying changed or new data. Differential backups are faster than full backups but slower than incremental backups since they copy all changed or new data since the last full backup.
Which backup method is better for data recovery?
- Incremental Backups: For recovery, you need the most recent full backup and all subsequent incremental backups. This method allows for a more granular recovery but can be time-consuming if you have many incremental backups.
- Differential Backups: For recovery, you only need the most recent full backup and the latest differential backup. This method simplifies the restore process but may occupy more storage space over time.
Can I combine incremental and differential backups in my backup strategy?
Yes, some backup solutions offer the flexibility to combine both methods in a single backup strategy. For example, you might perform daily incremental backups for short-term recovery and weekly differential backups for longer-term data retention. This hybrid approach balances storage efficiency and ease of recovery.
