When it comes to choosing a hard drive for your computer or storage needs, one of the most important factors to consider is the form factor. The form factor refers to the physical dimensions and specifications of a device, and in the case of hard drives, it determines the size and compatibility of the drive with various systems. In this blog post, we will explore and compare two common hard drive form factors: 2.5″ and 3.5″ drives, their characteristics, and the advantages they offer.
2.5" Drives
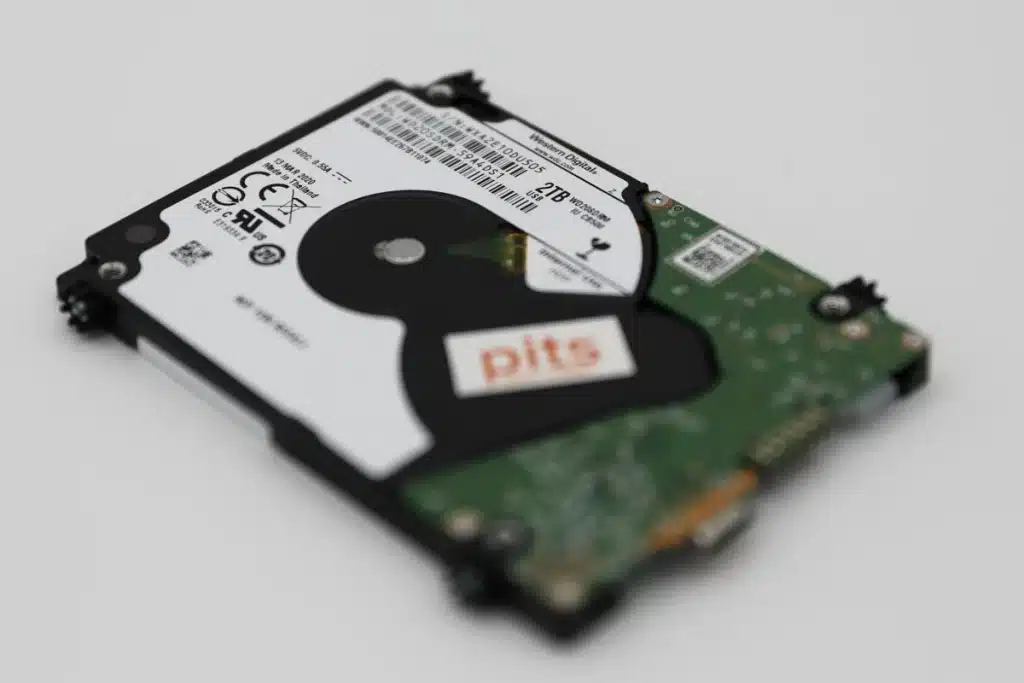
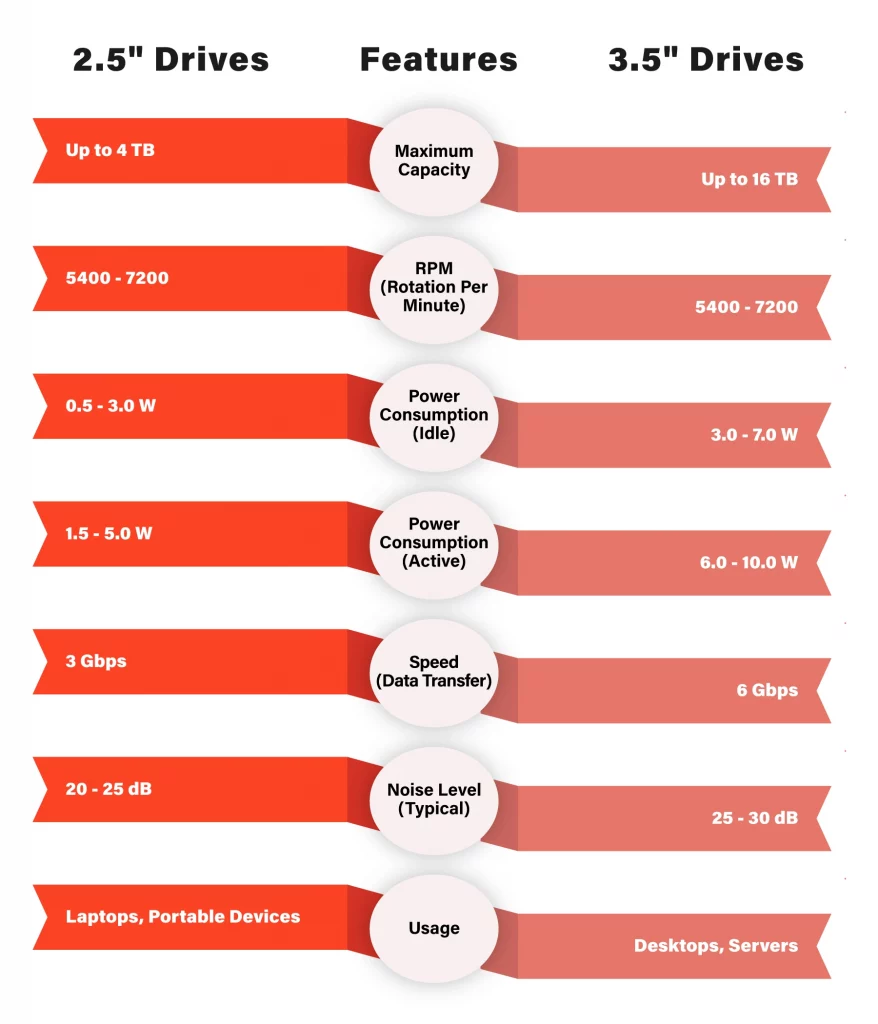
Let’s start by examining 2.5″ drives. As the name suggests, these drives have a diameter of 2.5 inches and are commonly used in laptops and portable devices. However, they can also be utilized in desktop systems and servers. The smaller physical size of 2.5″ drives makes them ideal for compact systems where space is limited, such as small form factor PCs or slim laptops.
One of the key advantages of 2.5″ drives is their portability. Due to their smaller size and lighter weight, they are more convenient for individuals who require mobility or need to carry their data with them. These drives are also popular for external storage solutions and are commonly used as backup drives or in portable hard drive enclosures.
Another important factor to consider is power consumption. 2.5″ drives typically consume less power compared to their larger counterparts. This makes them ideal for laptops, where battery life is a crucial consideration. Additionally, their lower power consumption also translates to reduced heat generation and improved energy efficiency.
In terms of performance, 2.5″ drives are available in both traditional hard disk drive (HDD) and solid-state drive (SSD) technologies.
While traditional HDDs offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost, SSDs provide faster data access speeds, better shock resistance, and lower latency. SSDs are especially popular in 2.5″ form factor due to their compact size and ability to withstand vibrations and impacts.

3.5" Drives
Moving on to 3.5″ drives, these larger form factor drives have a diameter of 3.5 inches and are primarily used in desktop systems and servers. They are commonly referred to as desktop hard drives. The larger physical dimensions of 3.5″ drives allow for more spacious internal components, including larger disk platters and additional features.
One of the significant advantages of 3.5″ drives is their higher storage capacity. The larger size allows for more disk platters to be accommodated within the drive, resulting in greater overall storage space. These drives are often preferred in desktop systems or servers where large amounts of data need to be stored, such as media libraries or databases.
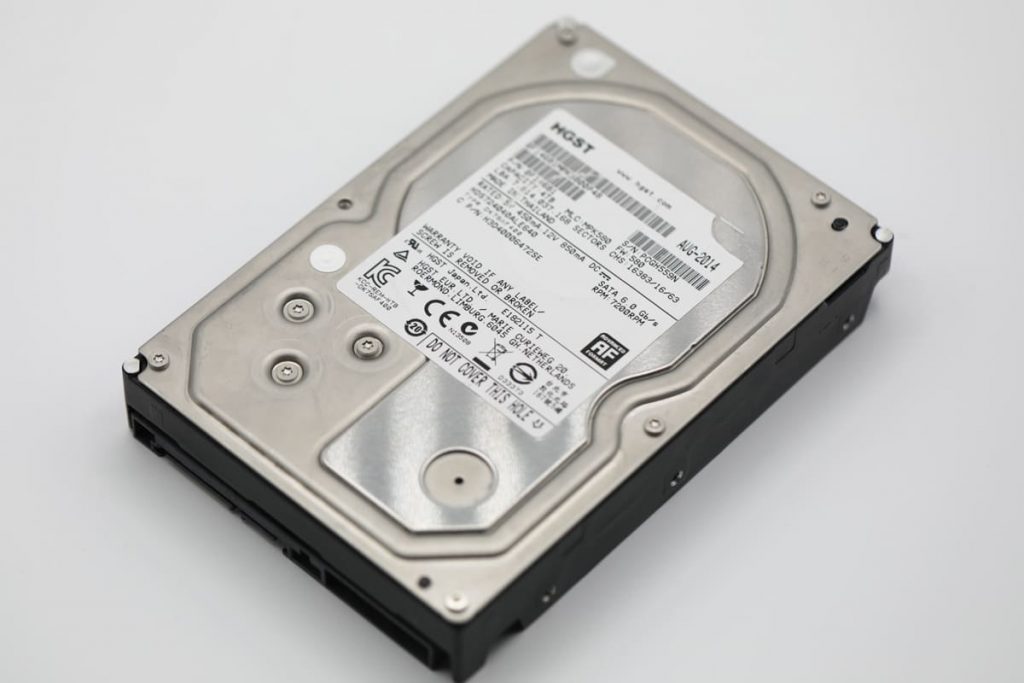

Another important factor to consider is the rotational speed of the drive. 3.5″ drives, especially those designed for desktop use, often offer faster speeds, with 7200 revolutions per minute (RPM) being a common specification. This increased rotational speed enables faster data transfer rates and reduced access times, making them suitable for applications that require high-performance storage, such as gaming or video editing.
Additionally, 3.5″ drives often come with advanced features such as built-in accelerometers, which can detect sudden movements or shocks. These accelerometers help protect the drive by triggering mechanisms that park the read/write heads to prevent data loss or damage during accidental drops or impacts. This feature is particularly beneficial in desktop systems where the risk of physical movement or mishandling is higher compared to laptops or portable devices.
2.5" vs. 3.5" Drives: Which is Right for You?
When deciding between 2.5″ and 3.5″ drives, several factors should be considered. If portability, power consumption, and shock resistance are essential to you, then a 2.5″ drive, especially an SSD, would be a suitable choice. They are perfect for laptops, external storage, or situations where space and power efficiency are critical.
On the other hand, if storage capacity, high performance, and advanced features like accelerometers are your priorities, then a 3.5″ drive would be a better option. They are ideal for desktop systems, servers, and applications that demand large storage space and fast data access.
Ultimately, the choice between 2.5″ and 3.5″ drives depends on your specific requirements and the intended use of the drive. It is worth noting that both form factors have their unique advantages and are designed to cater to different needs in various computing environments.
Understanding the differences between 2.5″ and 3.5″ hard drive form factors is crucial when selecting the right storage solution for your needs. While 2.5″ drives offer portability, lower power consumption, and shock resistance, 3.5″ drives provide higher storage capacity, faster speeds, and advanced features.
Whether you prioritize mobility and energy efficiency or require large storage capacities and high-performance capabilities, the form factor of your hard drive plays a significant role in meeting your specific requirements.
Consider the physical dimensions, power consumption, storage capacity, rotational speed, and advanced features when making your decision. By understanding these distinctions, you can make an informed choice and ensure that your storage solution aligns perfectly with your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between 2.5" drives and 3.5" drives
The main difference between 2.5″ drives and 3.5″ drives is their physical size. A 2.5″ drive has a smaller diameter of 2.5 inches, making it more suitable for laptops, portable devices, and compact systems. On the other hand, a 3.5″ drive has a larger diameter of 3.5 inches and is commonly used in desktop systems and servers.
Can I use a 2.5" drive in a desktop computer?
Yes, in most cases, you can use a 2.5″ drive in a desktop computer. Many desktop computer cases and drive bays are designed to accommodate both 2.5″ and 3.5″ drives. However, you may need a mounting adapter or bracket to securely fit the smaller 2.5″ drive into the larger 3.5″ drive bay.
Which drive form factor is better for portability?
If portability is a significant factor for you, then a 2.5″ drive is the better choice. Their smaller size and lighter weight make them more convenient for individuals who require mobility or need to carry their data with them. 2.5″ drives are commonly used in laptops and are popular for external storage solutions such as portable hard drive enclosures.
Are 2.5" drives less powerful or slower than 3.5" drives?
No, the physical size of the drive does not directly determine its power or performance. Both 2.5″ and 3.5″ drives are available in various technologies and can be either traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs). While SSDs generally offer faster data access speeds compared to HDDs, the power and performance of a drive depend on factors such as rotational speed (RPM) and technology (HDD or SSD).
Which drive form factor is better for high-capacity storage?
If you require high-capacity storage, a 3.5″ drive is generally the better option. The larger physical size of 3.5″ drives allows for more disk platters to be accommodated, resulting in greater overall storage space. They are commonly used in desktop systems and servers where large amounts of data need to be stored, such as media libraries or databases. However, it’s worth noting that high-capacity 2.5″ drives are also available, particularly in the form of SSDs, although they may be more expensive compared to their 3.5″ counterparts.
