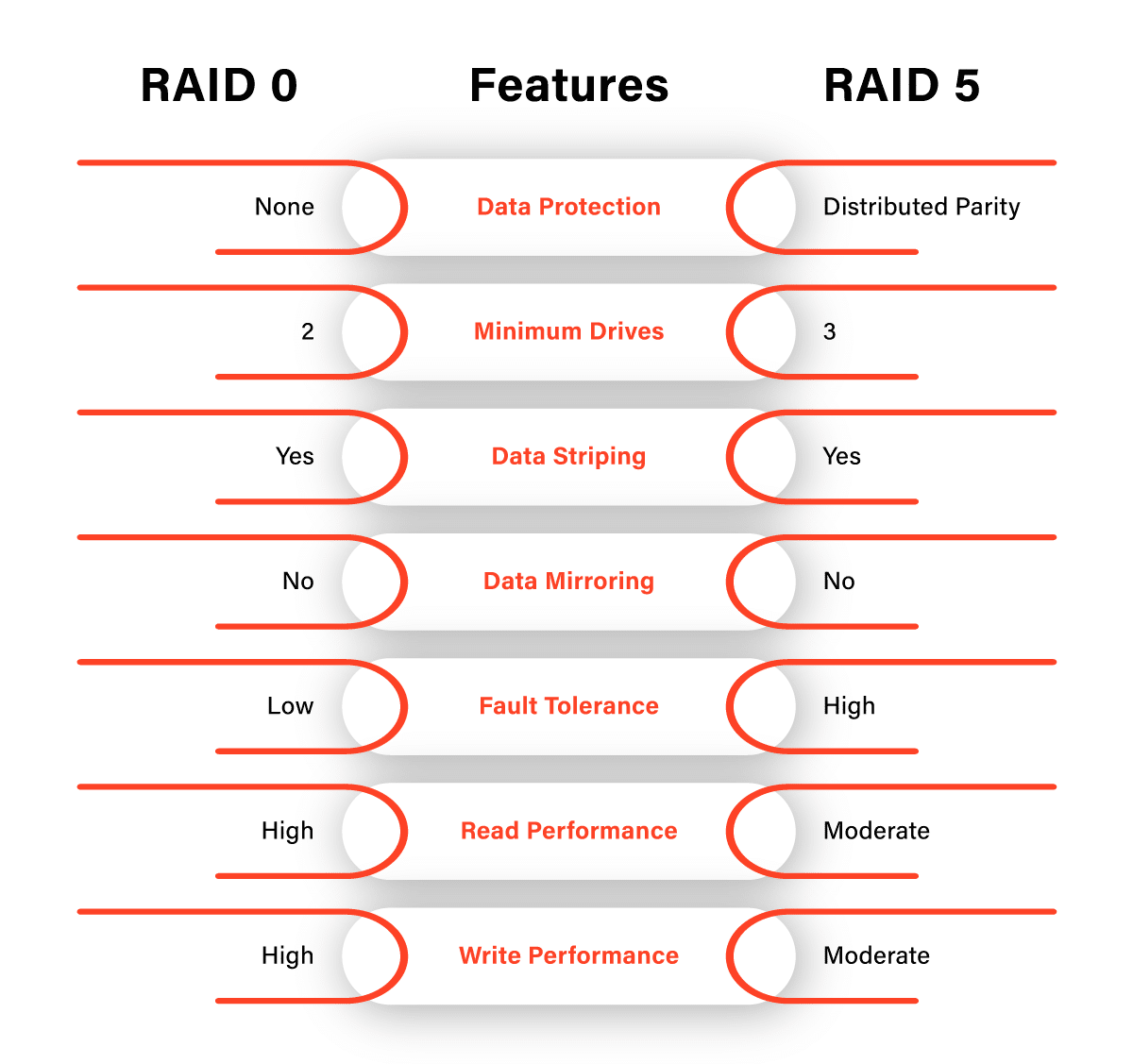
In the world of data storage and recovery, two RAID configurations stand out for their unique characteristics and capabilities – RAID 0 and RAID 5. At PITS Global Data Recovery Services, we understand the importance of selecting the right RAID configuration for your specific needs.
This blog post will delve deep into the world of RAID 0 and RAID 5, exploring the differences in speed, performance, and fault tolerance. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer picture of which RAID setup is best suited for your data storage requirements.
RAID Basics
Before we dive into the head-to-head comparison, let’s quickly recap what RAID is. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks and is a technology used to combine multiple hard drives into a single array for improved data storage, speed, and redundancy. RAID configurations vary, but the two we will focus on are RAID 0 and RAID 5.
RAID 0: The Need for Speed
RAID 0, often referred to as “striping,” is designed with one primary objective – speed. In a RAID 0 array, data is split across multiple drives, which leads to enhanced read and write speeds. The split data, known as “stripes,” is evenly distributed across the drives. As a result, read and write operations occur simultaneously, leading to significantly faster performance compared to a single drive setup.
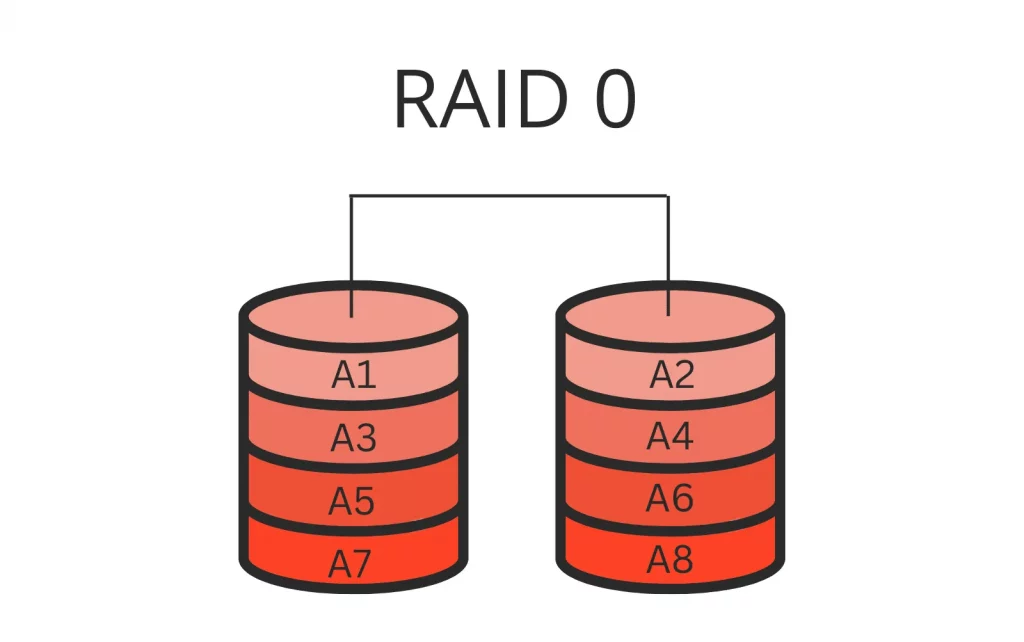
RAID 0 provides a significant boost in storage capacity since the total capacity is the sum of the individual drives in the array. However, this speed comes at a cost – fault tolerance. In a RAID 0 array, there is no redundancy.
If one drive fails, the entire array is at risk. This means that if you experience a drive failure, you may face total data loss.
RAID 5: The Balanced Approach
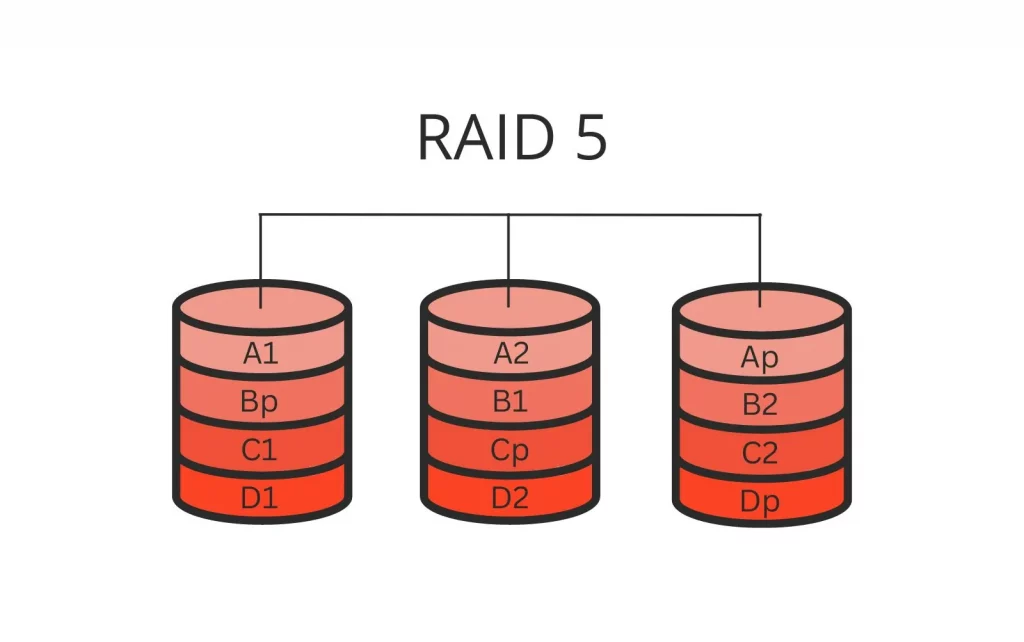
RAID 5 takes a more balanced approach, combining both speed and fault tolerance. In a RAID 5 array, data is distributed across multiple drives, just like RAID 0, but with a key difference – parity data. Parity data is used to reconstruct information in case of a drive failure. Each drive in the RAID 5 array stores a portion of this parity data, which ensures that if one drive fails, your data is still safe.
RAID 5 offers a good balance between speed and fault tolerance. The read-and-write performance is generally strong, and it can withstand the failure of a single drive without causing total data loss.
The storage capacity is also better compared to a single drive, although it’s less than that of RAID 0 since a portion of the total drive capacity is used for parity.
Speed Showdown: RAID 0 vs. RAID 5
When it comes to raw speed, RAID 0 takes the lead. Because of its striping mechanism, it excels in read and write operations. However, it is important to note that the actual performance increase varies depending on the number of drives in the array.
The more drives you add to a RAID 0 setup, the faster it becomes. If speed is your primary concern and you have a reliable backup system, RAID 0 might be a suitable choice.
On the other hand, RAID 5, while not as lightning-fast as RAID 0, offers a respectable compromise between speed and fault tolerance. The presence of parity data may slightly slow down write operations, but it ensures data integrity and minimizes the risk of total data loss in the event of a single drive failure.
RAID 5 vs. RAID 0 Performance Analysis
To get a more nuanced understanding of performance, let’s consider write operations and their impact on RAID 0 vs RAID 5 performance:
RAID 5 vs. RAID 0 Speed
RAID 0 is exceptional when it comes to write speed since data is written across all drives simultaneously. This makes it ideal for tasks like video editing and gaming where rapid data transfer is crucial.

RAID 5, while not as fast as RAID 0, still offers solid write performance. The presence of parity data introduces some overhead, but this is often offset by the redundancy it provides.
RAID 5 vs. 0 Fault Tolerance
RAID 0 offers no fault tolerance. If a single drive fails in the array, you risk losing all the data. This configuration is suitable for non-critical, high-speed applications where data can be quickly restored from backups.
RAID 5, with its parity data, can withstand the failure of a single drive. This is especially important in business environments where data integrity is critical, and downtime can be costly.
Storage Capacity
RAID 0 provides a straightforward way to increase storage capacity. The total capacity is the sum of all drives in the array. If you need ample space for data, RAID 0 is a strong contender.
RAID 5 also increases storage capacity but at the expense of some capacity allocated for parity data. The total capacity is less than the sum of all drives but offers a balance between capacity and redundancy.
RAID Configurations: RAID 0 vs. 5 vs. Others
It is important to mention that RAID 0 and RAID 5 are just two options among many RAID configurations. There’s also RAID 6 array, which offers a higher level of fault tolerance by allowing the failure of two drives, and RAID 1 array, which is known for its mirroring capabilities, providing redundancy by duplicating data across drives.

Additionally, RAID can be implemented through both hardware RAID controllers and software RAID setups. Hardware RAID typically requires a dedicated RAID controller, while software RAID is managed by the operating system. The choice between hardware and software RAID depends on factors such as cost, ease of management, and performance requirements.
In the battle of RAID 0 vs. RAID 5, the choice ultimately comes down to your specific needs and priorities.
If you demand sheer speed and are willing to accept the risk of total data loss, RAID 0 is your best bet. However, if you require a balance between speed and fault tolerance, RAID 5 is the way to go. It can handle the failure of a single drive without compromising your data.
PITS Global Data Recovery Services understands the importance of selecting the right RAID configuration. We’re here to help you make informed choices about your data storage solutions and provide expert assistance in the event of data loss. Whether you choose RAID 0, RAID 5, or any other configuration, our data recovery experts are ready to step in if the unexpected happens, ensuring your data remains secure and accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary advantage of RAID 0?
RAID 0 striping, offers exceptional speed, as data is split and simultaneously read and written across multiple drives in the array.
How does RAID 5 balance speed and fault tolerance?
RAID 5 distributes data across drives with the added benefit of parity data, allowing it to recover data in case of a single drive failure while maintaining good performance.
What are the performance differences between RAID 0 and RAID 5, particularly in write speed?
RAID 0 excels in write speed as data is written across all drives simultaneously. RAID 5 provides solid write performance but introduces some overhead because of parity data.
Is fault tolerance crucial when choosing between RAID 0 and RAID 5?
Yes, fault tolerance is a critical consideration. RAID 0 offers no fault tolerance, making it suitable for non-critical applications, while RAID 5 can withstand a single drive failure, making it more suitable for business environments.
How does storage capacity differ between RAID 0 and RAID 5?
RAID 0 provides maximum storage capacity as the total is the sum of all drives. RAID 5 also increases capacity but allocates some space for parity data, resulting in a slightly lower total capacity.
Are there other RAID configurations to consider?
Yes, besides RAID 0 and RAID 5, there are configurations like RAID 6, which offers higher fault tolerance, and RAID 1, known for its mirroring capabilities. The choice depends on your specific needs.
