In the world of computer storage, there are several options available to consumers, each with their own unique advantages and disadvantages. Two of the most popular options are the Solid State Drive (SSD) and the Solid State Hybrid Drive (SSHD). This article explores the differences between hybrid storage vs. SSD and help you decide which one is best for you.
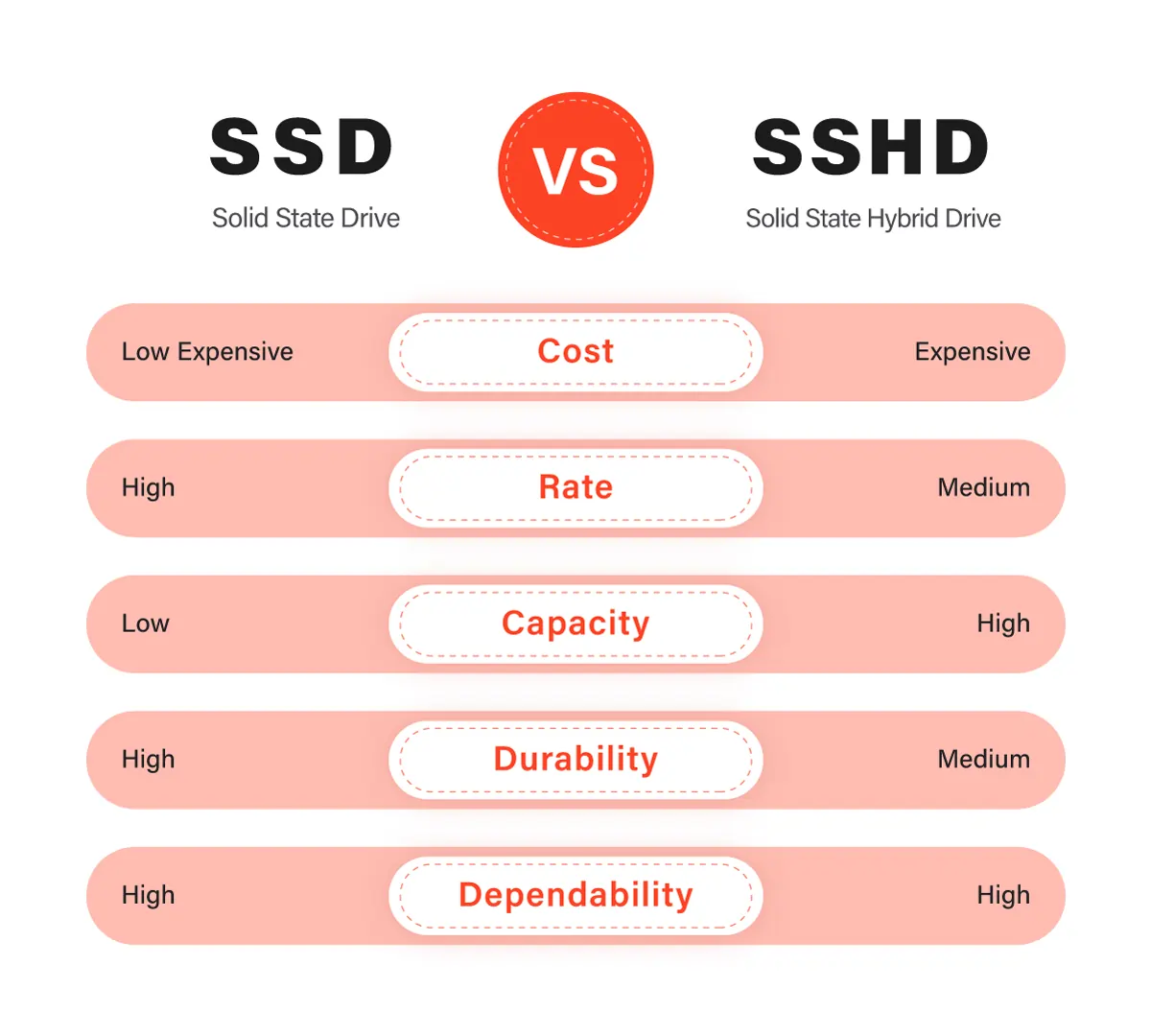
SSD vs. SSHD - Main Difference Between SSD and SSHD
Hybrid SSHD vs. SSD are both storage devices that offer different benefits depending on the user’s needs. SSDs are faster and more reliable than SSHDs because they have no moving parts and use flash memory technology. This structure makes them ideal for high-performance tasks such as gaming and video editing. They also consume less power and generate less heat, which is beneficial for laptops and other portable devices.
On the other hand, SSHDs combine the speed of an SSD with the larger storage capacity of a traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD). This makes them a cost-effective option for users who require a high capacity but cannot afford the high cost of an SSD. SSHDs use a combination of a small amount of flash memory and a larger HDD to store frequently accessed data, which results in faster boot times and application load times.
What is an SSD?
SSDs are built using high-performance NAND flash memory and a solid-state storage architecture. This allows them to read and write data much faster than traditional HDDs. In addition to being faster, SSDs are also more energy-efficient, generate less heat, and are quieter than traditional hard drives. SSDs have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their high-speed performance, durability, and lower risk of data loss.
The solid-state technology also allows to have a smaller physical footprint, making them ideal for use in laptops. However, SSDs can be more expensive than traditional hard drives, and their storage capacity may be limited in comparison. As with any technology, it is important to consider the specific needs of your operating system and usage requirements to determine, whether to choose hybrid HDD vs. SSD.
How Does an SSD Work and How Do You Use It?
An SSD works by using a series of interconnected memory chips to store data in a process known as flash memory. These memory chips are made up of high-performance NAND flash memory, which allows for fast and efficient read and write operations.
When a file is saved to an SSD, the data is broken down into small blocks and written to the available memory cells on the chip. When a user requests to access the file, the SSD retrieves the data from the memory chips and sends it to the computer’s processor for use. To use an SSD, you must connect it to your computer using a compatible interface, such as a SATA drive, NVMe, or PCIe.

Once connected, you can use it like any other storage device, saving files and installing applications as you normally would. However, it is important to note that SSDs have a finite lifespan and can only be written to a certain number of times before they wear out.
To maximize the lifespan of your SSD, it is recommended to avoid writing large amounts of data continuously and to enable features such as TRIM to help manage the storage and maintain performance over time.
What is an SSHD?
An SSHD utilizes high-performance NAND flash memory operations to provide faster data access for frequently used files. This technology allows the SSHD to function as a regular hard disk drive while offering some of the benefits of an SSD.
The SSHD automatically moves frequently accessed files to the solid-state storage portion, allowing them to be accessed quickly. In contrast, less frequently used files are stored on the traditional hard drive portion. This process is managed by the device’s firmware, which intelligently decides which files should be stored on the solid-state portion. To use an SSHD, you simply install it in your computer or device like you would a traditional hard drive.
The operating system and applications interact with the SSHD the same way they would with a traditional hard drive. The user does not need to manage the storage on the SSHD, as the device’s firmware automatically handles the data migration between the solid-state and traditional storage areas. The user only needs to be aware of the overall storage capacity of the device, which will depend on the size of the solid-state and traditional portions of the drive.
How Does an SSHD Work and How Do You Use it?
To optimize the performance of an SSHD, the drive uses a special algorithm that analyzes which files and applications are used most frequently. The algorithm then automatically moves those files and applications to the solid-state storage for faster access.
Over time, the algorithm learns which data is accessed most frequently and adjusts the data placement accordingly.
Using an SSHD is very similar to using a traditional hard drive. You can save files to it, install applications on it, and access data stored on it. The only difference is that the SSHD will automatically optimize overall performance by storing frequently accessed data on the solid-state storage.
However, it is worth noting that the solid-state storage on an SSHD is typically smaller than that of a standalone SSD, so you may not see the same level of performance as you would with a full SSD.
When choosing between a hybrid hard drive vs. SSD, it is important to consider your budget, storage needs, and the tasks you will be performing. SSDs are generally more expensive but offer faster read and write speeds, making them ideal for demanding tasks. SSHDs, on the other hand, are more affordable and offer a larger storage capacity, making them suitable for everyday use.
Ultimately, the decision between SSD vs. hybrid hard drive comes down to your specific needs and preferences. Both options have their own advantages and disadvantages, and it is up to you to determine which one is the best fit for your computing needs. By understanding the differences between hybrid drive vs. SSD, you can make an informed decision and choose the storage solution that meets your needs and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an SSHD and an SSD?
- SSD (Solid-State Drive): An SSD uses NAND flash memory to store data. It has no moving parts, which results in faster data access, lower power consumption, and greater durability. SSDs are known for their speed and reliability.
- SSHD (Solid-State Hybrid Drive): An SSHD combines traditional spinning hard drive (HDD) technology with a small amount of NAND flash memory. This hybrid design aims to provide the capacity of an HDD and some of the speed benefits of an SSD.
Which is faster, an SSHD or an SSD?
SSDs are generally much faster than SSHDs. Since SSDs have no moving parts and use NAND flash memory, they offer significantly faster data read and write speeds, resulting in quicker boot times and application load times.
What are the advantages of choosing an SSD over an SSHD?
- Speed: SSDs offer faster data access and transfer speeds, improving overall system performance.
- Durability: SSDs have no moving parts, making them more resistant to physical shocks and less susceptible to mechanical failures.
- Energy Efficiency: SSDs consume less power, leading to longer battery life in laptops and reduced energy costs for desktops.
- Silent Operation: SSDs produce no noise since they lack moving components.
How do I choose between an SSD and an SSHD for my computer?
- Choose an SSD: If speed and performance are your top priorities, and you can sacrifice some storage capacity for those benefits, go for an SSD. SSDs are ideal for operating systems and frequently used applications.
- Choose an SSHD: If you need a balance between speed and storage capacity and have budget constraints, an SSHD can be a good compromise. SSHDs are suitable for users who need a lot of storage but still want improved performance compared to traditional HDDs.
Can PITS Global Data Recovery Services assist with data recovery for both SSDs and SSHDs?
Yes, PITS Global Data Recovery Services has expertise in recovering data from both SSDs and SSHDs. If you experience data loss on either of these storage devices, our team can help you recover your valuable data.